Todd Villines, M.D., FACC, FAHA, MSCCT, explains some of the discussion on CT used for COVID-19 patients at the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT) 2020 virtual meeting in July. He is the Julian Ruffin Beckwith Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Virginia; editor-in-chief of the Journal of Cardiovascular CT (JCCT), and SCCT past-president.
Early on in the COVID-19 pandemic in China, CT emerged as a key imaging modality and was found to be able to detect COVID ground glass lesions in the lungs sometimes prior to positive genetic PCR test results. Supporters of CT say the modality offers a way to get detailed anatomical and functional information using a short exam time and limits the exposure of staff to potential or known COVID-19 positive patients.
One area where cardiac CT is seeing a lot of increased his is for the evaluation of thrombus in the left atrial appendage (LAA). This is traditionally done using trans esophageal echo (TEE), but it required very close contact with the patient and direct exposure of staff to bodily fluids and potential viral shed from the patient exhaling with each breath.
Related CT During COVID-19 Content:
Cardiac Imaging Best Practices During the COVID-19 Pandemic
VIDEO: CT and POCUS Emerge As Frontline Cardiac Imaging Modalities in COVID-19 Era — Interview with Geoffrey Rose, M.D.,
ASE Guidelines for the Protection of Echocardiography Providers During the COVID-19 Outbreak
Study Looks at CT Findings of COVID-19 Through Recovery
Experts Stress Radiology Preparedness for COVID-19
ACR Recommendations for the Use of Chest Radiography and CT for Suspected COVID-19 Cases
Other Key Trends and CT Technology at SCCT:
Top 9 Cardiovascular CT Studies in Past Year
VIDEO: Photon Counting Detectors Will be the Next Major Advance in Computed Tomography
VIDEO: Coronary Plaque Quantification Will Become Major Risk Assessment
VIDEO: Key Cardiac CT Papers Presented at SCCT 2020
Low-attenuation Coronary Plaque Burden May Become Next Big Cardiac Risk Assessment
Impact of Cardiac CT During COVID-19
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence to Automate CT Calcium Scoring and Radiomics





















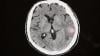
 The software also offers a second set of eyes for more difficult to detect cases. Quickly determining is a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic is critical to the path of treatment. If caught early enough, TPA can be injected into patients to clear clots causing an ischemic stroke, but can cause massive brain damage or death if injected into a patient with a brain bleed. At advanced neuro-interventional centers, quickly determining the type of stroke is needed to know if they need to revascularize a patient or manage a hemorrhage.
The software also offers a second set of eyes for more difficult to detect cases. Quickly determining is a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic is critical to the path of treatment. If caught early enough, TPA can be injected into patients to clear clots causing an ischemic stroke, but can cause massive brain damage or death if injected into a patient with a brain bleed. At advanced neuro-interventional centers, quickly determining the type of stroke is needed to know if they need to revascularize a patient or manage a hemorrhage. 
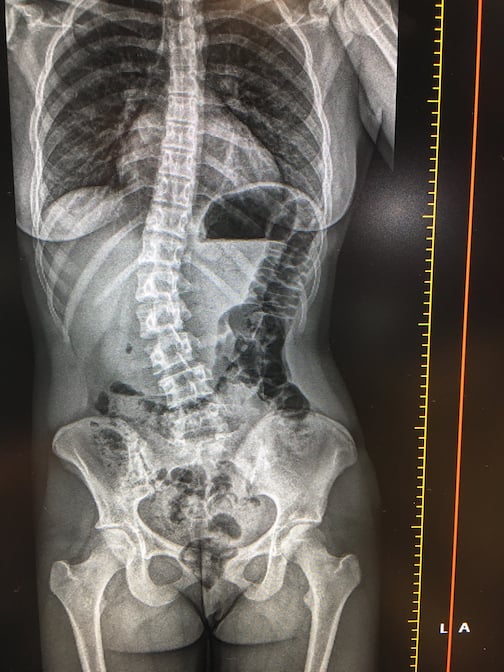 This is a demo of the EOS orthopedic X-ray imaging system at the recent 2019
This is a demo of the EOS orthopedic X-ray imaging system at the recent 2019