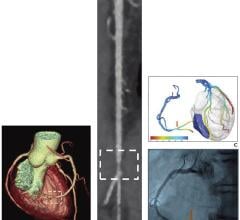
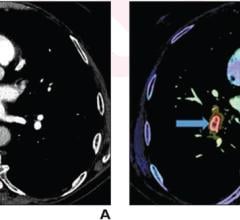
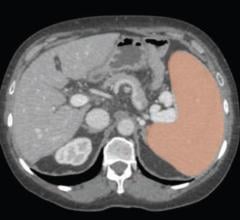
June 29, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) ...
Computed Tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (CT) systems use a series of X-ray images to create an image volume dataset with slices that can be manipulated on any plane using advanced visualization software. The section includes computed tomography scanners, CT contrast agents, CT angiography (CTA and CCTA), CT perfusion, spectral CT (dual-source CT), and iterative reconstruction dose reduction software.
June 22, 2023 — New ultra-high-resolution CT technology enables excellent image quality and accurate diagnosis of ...
June 16, 2023 — iCRco, Inc., a leading provider of advanced medical imaging solutions, is proud to announce the 4 year ...
SPONSORED CONTENT — Fujifilm’s latest CT technology brings exceptional image quality to a compact and user- and patient ...
June 13, 2023 — The Cancer Institute at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital is the first in New York State to use the ...
June 9, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) ...
June 7, 2023 — Riverain Technologies, a medical device company revolutionizing chest imaging interpretation with Clear ...
In June, the Philips Radiology Experience Tour hit the road to provide healthcare professionals with an opportunity to ...
May 26, 2023 — GE HealthCare, a leading medical technology innovator, announced today its largest ever CT deal in the ...
May 24, 2023 — A new advanced form of computed tomography (CT) imaging called photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) ...
May 19, 2023 — Asymptomatic adults with a high accumulation of fat in their muscles, known as myosteatosis, are at an ...
This summer, the Philips Radiology Experience Tour has been bringing Philips imaging modalities directly to the ...
May 18, 2023 — Royal Philips, a global leader in health technology, announced the launch of the Philips CT 3500, a new ...
May 17, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), SARS ...
May 5, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a high ...
The healthcare industry faces many different types of obstacles in today’s challenging marketplace. Staff shortages ...
In the past year, the radiology community has been a first-hand, hands-on witness to myriad unexpected challenges and ...
Modalities used in spine surgery, like computed tomography (CT) scan-based navigation systems and even X-rays, reached a ...
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technology that has been around for more than four decades and is a staple in ...
April 21, 2023 — GE HealthCare is further advancing its precision care strategy with CT-Navigation, which offers ...
April 20, 2023 — The American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is pleased to announce that The Roentgen Fund 2023 Honorary ...
April 5, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a ...
Yet another month has flown by, and we are taking a look at the content our viewers found most interesting during the ...
March 31, 2023 — Philips, a global leader in health technology, and Connally Memorial Medical Center (CMMC), today ...

 June 29, 2023
June 29, 2023