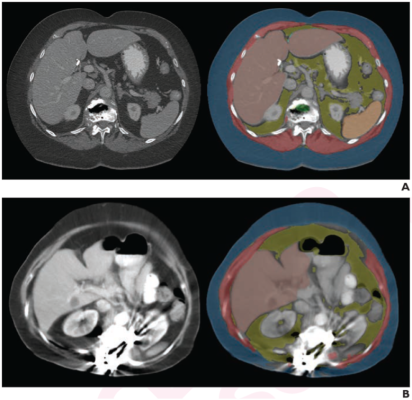
Examples of Specific Causes Identified for AI Tool Failure. Axial images at L1 level, without (left) and with (right) segmentation overlay. Red indicates skeletal muscle, green indicates trabecular bone, yellow indicates visceral fat, and blue indicates subcutaneous fat. Segmented regions also include liver (beige) and spleen (orange), which were not evaluated as part of present analysis. (A) 78-year-old woman who underwent abdominopelvic CT at outside institution. Bone tool returned L1 vertebral body bone attenuation of -146 HU, outside of reference range. Thus, tool was deemed technical failure for bone tool. Failure was attributed to volume averaging of vacuum phenomenon within slice. (B) 64-year-old woman who underwent abdominopelvic CT at outside institution. Bone tool returned vertebral body bone attenuation of -10,000 HU (default value for segmentation failure detected by tool), outside of reference range. Thus, tool was deemed technical failure for bone tool. Failure was attributed to presence of spinal fusion hardware.
February 22, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), certain reasons for AI tool failure relating to technical factors may be largely preventable through proper acquisition and reconstruction protocols.
“The automated AI body composition tools had high technical adequacy rates in a heterogeneous sample of external CT examinations, supporting the tools’ generalizability and potential for broad use,” concluded head researcher B. Dustin Pooler, MD, from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health in Madison.
This AJR accepted manuscript included 8,949 patients (mean age, 55.5 years; 4,256 men, 4,693 women) who underwent abdominal CT—performed at different institutions on different scanners from different manufacturers—subsequently transferred to the local PACS for clinical purposes. Deploying three independent automated AI tools to assess body composition via bone attenuation, muscle amount and attenuation, as well as visceral and subcutaneous fat amounts, one axial series per examination was evaluated.
Ultimately, three fully automated AI tools for measuring body composition (vertebral bone, body wall musculature, and visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat) had technical adequacy rates of 97.8%- 99.1% on Pooler et al.’s sample of 11,699 external abdominal CT examinations—performed at 777 different external institutions using 82 different scanner models from 6 different manufacturers.
Noting that reasons for failure also included factors inherent to patients that are more challenging to control, “explainability and an understanding of reasons for failure can help build trust in AI tools and increase acceptance among radiologists and other physicians,” the authors of this AJR accepted manuscript added.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026