June 25, 2024 — Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego, one of the nation’s top pediatric health care systems, today ...
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI creates images from the magnetic resonance created in hydrogen atoms when they are polarized and an electromagnetic pulse is used to knock them off axis. This section includes MR analysis software, MRI scanners, gadolinium contrast agents and related magnetic resonance imaging accessories.
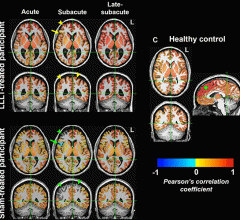
June 25, 2024 — The structural and functional organization of the brain as shown on MRI can predict the progression of ...
June 17, 2024 — MRI has transformed neuroscience research over the past 50 years, but research participants have had to ...
Fujifilm’s APERTO Lucent is a 0.4T mid-field, open MRI system addressing today’s capability and image quality needs ...
June 12, 2024 — Royal Philips recently announced the 1,111th installation of its revolutionary BlueSeal 1.5T magnet ...
June 3, 2024 — MRI scans are commonly used to diagnose a variety of conditions, anything from liver disease to brain ...
May 31, 2024 — Low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain ...
In June, the Philips Radiology Experience Tour hit the road to provide healthcare professionals with an opportunity to ...
May 29, 2024 — Strategic Radiology added a third California member to the nation’s leading coalition of independent ...
May 14, 2024 — University Hospitals (UH) and Siemens Healthineers announce a 10-year strategic alliance that builds on ...
May 13, 2024 — Avenda Health, an AI healthcare company creating the future of personalized prostate cancer care, unveils ...
This summer, the Philips Radiology Experience Tour has been bringing Philips imaging modalities directly to the ...
May 13, 2024 — National Basketball Association (NBA), the National Basketball Players Association (NBPA), and the Next ...
May 7, 2024 — The Magna Cum Laude Award-Winning Online Poster presented during the 124th ARRS Annual Meeting showed a ...
May 6, 2024 — GE HealthCare has announced the unveiling of its SIGNA MAGNUS[i], an FDA 510(k) pending head-only magnetic ...
The healthcare industry faces many different types of obstacles in today’s challenging marketplace. Staff shortages ...
May 6, 2024 — Elekta announced the acquisition of Philips Healthcare’s Pinnacle Treatment Planning System (TPS) patent ...
May 6, 2024 — Hvidovre Hospital has the world's first prototype of a sensor capable of detecting errors in MRI scans ...
Beginning this spring, ITN will begin sending out a bi-monthly survey to our readers on a variety of topics, which we ...
April 29, 2024 — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced Elekta Instrument AB is recalling Disposable ...
April 24, 2024 — A new study from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare ...
April 23, 2024 — A diverse writing group, led by authors at the University of Toronto, have developed an approach for ...
April 17, 2024 — VISTA.AI announced the appointment of Daniel Hawkins as President and CEO. The company is pioneering AI ...
April 17, 2024 — Hyperfine, Inc., a groundbreaking health technology company that has redefined brain imaging with the ...


 June 25, 2024
June 25, 2024