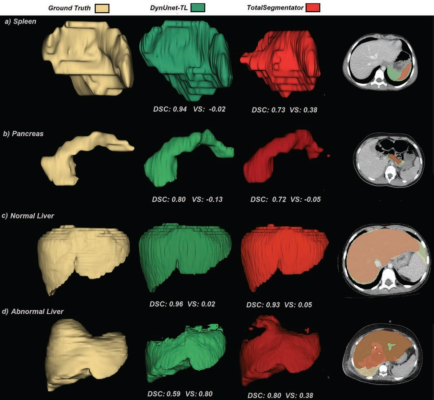
Ground-truth manual organ segmentations (yellow) vs. DynUNet-TL (green) and TotalSegmentator (red) predictions. For all four patients, final image is representative axial CT slice, showing segmentations. (A) Segmentation of normal spleen in 5-year-old girl from LS-pediatric test set. Performance was better for DynUNet-TL than for TS (DSC: 0.94 vs 0.73; VS: -0.02 vs 0.38). (B) Segmentation of normal pancreas in 11-year-old girl from P-pediatric test set. Performance was similar between DynUNet-TL and TS (DSC: 0.80 vs 0.72; VS: -0.13 vs -0.05). (C) Segmentation of normal liver in 6-year-old girl from LS-pediatric test set. Performance was similar between DynUNet-TL and TS (DSC: 0.96 vs 0.93; VS: 0.02 vs 0.05). (D) Segmentation of abnormal liver from 15-year-old boy from Total Cancer Imaging Archive pediatric test set. Patient had large liver tumor. Performance was worse for DynUNet-TL than for TS (DSC: 0.59 vs 0.80; VS: 0.80 vs 0.38). DSC: Dice similarity coefficient, VS: volume similarity
May 15, 2024 — Transfer learning (TL) models trained on heterogeneous public datasets and fine-tuned using institutional pediatric data outperformed internal native training (NT) models and TotalSegmentator (TS) across internal and external pediatric test data, according to the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
“The best-performing organ segmentation model, based on internal and external validation, is now available as an open-source application for further research and potential clinical deployment,” noted first author Elanchezhian Somasundaram, PhD, from the radiology department at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
In their AJR accepted manuscript, Somasundaram et al. developed and validated deep-learning models for liver, spleen, and pancreas segmentation using 1,731 CT examinations (1,504 training; 221 testing), derived from three internal institutional pediatric (age ≤ 18) datasets (n = 483) and three public datasets comprising pediatric and adult examinations with various pathologies (n = 1,248). Three deep-learning model architectures (SegResNet, DynUNet, SwinUNETR) from the Medical Open Network for AI (MONAI) framework underwent training using NT, relying solely on institutional datasets, and TL, incorporating pre-training on public datasets. For comparison, TS, a publicly available segmentation model, was applied to test data without further training.
Ultimately, the AJR authors’ optimal model outperformed models trained using only internal pediatric data, as well as a publicly available model. Acknowledging that segmentation performance was better in liver and spleen than in pancreas, “the selected model may be used for various volumetry applications in pediatric imaging,” Somasundaram et al. concluded.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026