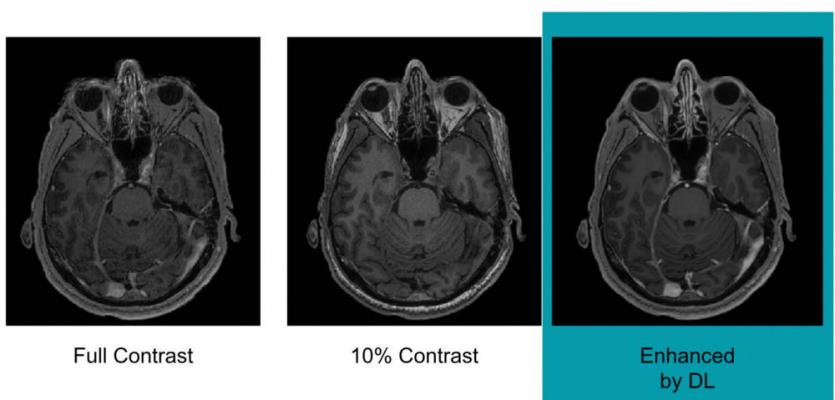
Example of full-dose, 10 percent low-dose and algorithm-enhanced low-dose. Image courtesy of Enhao Gong, Ph.D.
One of the most controversial issues in radiology in recent years has been the use of gadolinium as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams. Some studies and high-profile cases have suggested trace amounts of gadolinium are retained in the body after an exam and may cause a number of side effects, including nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in the kidneys. A recent study out of Stanford University demonstrated how the need for gadolinium contrast could be reduced or eliminated by using artificial intelligence (AI)-based image reconstruction.
“There is concrete evidence that gadolinium deposits in the brain and body,” said study lead author Enhao Gong, Ph.D. “While the implications of this are unclear, mitigating potential patient risks while maximizing the clinical value of the MRI exams is imperative.”
Gong and colleagues created a deep learning algorithm, a form of AI, to analyze MRI datasets. With deep learning, a computer algorithm is shown large amounts of data and learns to recognize patterns and features in an image. The goal in radiology is for the computer to be able to identify critical findings in an image more or as quickly as a human radiologist.
For this particular study, the algorithm was shown MR images from 200 patients who had received contrast-enhanced MRI scans for a variety of indications. Three sets of images were collected for each patient:
• Pre-contrast scans, done prior to contrast administration and referred to as the zero-dose scans;
• Low-dose scans, acquired after 10 percent of the standard gadolinium dose administration; and
• Full-dose scans, acquired after 100 percent dose administration.
Using this methodology allowed the algorithm to learn the difference between full- and low-dose administration, with the pre-contrast scans used as a control. With this knowledge at hand, the algorithm was able to reconstruct an image as if it was a full-dose scan from a 10 percent dose image. Study results showed there was no significant difference between an actual full-dose image and a reconstructed full-dose image.
Gong and colleagues said their study results indicate that eventually, the need for full dose gadolinium contrast could be eliminated. “Low-dose gadolinium images yield significant untapped clinically useful information that is accessible now by using deep learning and AI,” he said.
Equally important as the research findings themselves was validating the outputs of the algorithm, because radiologists need to be able to trust the results they are receiving. The research team employed quantitative metrics to evaluate the improvement of the enhanced contrast via deep learning, including peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), root mean square error (RMSE) and structural similarity index (SSIM). Qualitative metrics like image quality and contrast enhancement quality were used to assess the results of the deep learning-based enhancement. A non-inferiority test was used to assess the performance of the AI method and validate the ability to reduce contrast dose without sacrificing image quality. “We showed that it’s doing a certain type of enhancement or denoising on the subtraction level. But the subtraction is not done manually because the algorithm learns how to do subtraction and enhancement. So the signal was already in there, but the human eye cannot see the difference — but the algorithm can,” said Gong.
The next steps involve deploying the algorithm in a clinical setting, where Gong believes it will see its greatest utility. He said the algorithm will be tested across a wider range of MRI scanners, and even with other contrast agents besides gadolinium. “We’re not trying to replace existing imaging technology,” he said. “We’re trying to improve it and generate more value from the existing information while looking out for the safety of our patients.”
Gong received a Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) “Trainee Research Prize — Resident” award for his research, which was presented at the RSNA 2018 annual meeting last November.
Related Content of MRI Gadolinium Safety Concerns
The Debate Over Gadolinium MRI Contrast Toxicity
VIDEO: How Serious is MRI Gadolinium Retention in the Brain and Body? An interview with Max Wintermark, M.D.
VIDEO “Big Concerns Remain for MRI Gadolinium Contrast Safety at RSNA 2017,” An interview with Emanuel Kanal, M.D.
Radiology Has Failed to Properly Assess or Track MRI Gadolinium Contrast Safety
Recent Developments in Contrast Media
FDA Committee Votes to Expand Warning Labels on Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents
European Medicines Agency Issues Update on Gadolinium Contrast Agents
ISMRM Issues Guidelines for MRI Gadolinium Contrast Agents
FDA: No Harm in MRI Gadolinium Retention in the Brain
VIDEO: MRI Gadolinium Contrast Retention in the Brain
Gadolinium May Remain in Brain After Contrast MRI


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026