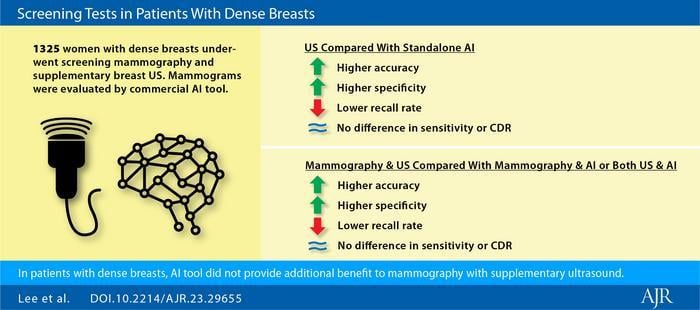
“Mammography with supplementary ultrasound showed higher accuracy, higher specificity, and lower recall rate in comparison to mammography with AI, as well as in comparison to mammography with both US and AI,” wrote corresponding author Hee Jung Moon, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at South Korea’s Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine. Image courtesy of American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
July 31, 2023 — Findings from an accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) suggest that for patients with dense breasts undergoing screening in the incidence setting, a commercial AI tool did not provide additional benefit to mammography with supplementary ultrasound (US).
“Mammography with supplementary ultrasound showed higher accuracy, higher specificity, and lower recall rate in comparison to mammography with AI, as well as in comparison to mammography with both US and AI,” wrote corresponding author Hee Jung Moon, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at South Korea’s Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine.
This AJR accepted manuscript included 1,325 women (mean age, 53 years) with dense breasts who underwent both screening mammography and supplementary breast US within a 1-month interval from January 2017 to December 2017; prior mammogram and US were available to compare in 91.2% and 91.8%, respectively. Fifteen radiologists (5 staff and 10 fellows) interpreted mammography and US examinations, and clinical reports were used for Moon et al.’s analysis. A commercially available AI algorithm (Lunit INSIGHT, v 1.1.0.0, Seoul, Korea) was used to retrospectively evaluate mammographic examinations for cancer presence. Then, screening performances were compared among mammography, AI, US, and test combinations, using generalized estimating equations. At least 24 months of imaging stability was required for a benign diagnosis.
Ultimately, mammography with AI, mammography with US, and mammography with both ultrasound and AI showed recall rate of 14.9, 11.7, and 21.4 (all p < .05); sensitivity of 83.3%, 100.0%, and 100.0% (all p > .05); specificity of 85.8%, 89.1%, and 79.4% (all p < .05); and accuracy of 85.7%, 89.2%, and 79.5% (all p < .05).
For more information: www.arrs.org
Related Breast Density Content:
VIDEO: FDA Update on the US National Density Reporting Standard - A Discussion on the Final Rule
One on One … with Wendie Berg, MD, PhD, FACR, FSBI
Task Force Issues New Draft Recommendation Statement on Screening for Breast Cancer
Creating Patient Equity: A Breast Density Legislative Update
AI Provides Accurate Breast Density Classification
VIDEO: The Impact of Breast Density Technology and Legislation
VIDEO: Personalized Breast Screening and Breast Density
VIDEO: Breast Cancer Awareness - Highlights of the NCoBC 2016 Conference
Fake News: Having Dense Breast Tissue is No Big Deal
The Manic World of Social Media and Breast Cancer: Gratitude and Grief
Related Breast Imaging Content:
Single vs. Multiple Architectural Distortion on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Today's Mammography Advancements
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Spot Compression Clarifies Ambiguous Findings
AI DBT Impact on Mammography Post-breast Therapy
ImageCare Centers Unveils PINK Better Mammo Service Featuring Profound AI
Radiologist Fatigue, Experience Affect Breast Imaging Call Backs
Fewer Breast Cancer Cases Between Screening Rounds with 3-D Mammography
Study Finds Racial Disparities in Access to New Mammography Technology


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026 









