"Our study demonstrates that a real-world lung cancer screening can perform similar to randomized controlled trials in regard to important performance metrics," the UPenn authors of this AJR article concluded. Image courtesy of American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
July 17, 2020 — An online first accepted manuscript published in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) finds that focusing on lung cancer screening (LCS) subjects less likely to remain in the program — those with negative low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) exams and those who still smoke — can improve that program's cost-effectiveness and maximize its societal benefits.
For people with a long history of smoking, LDCT LCS has been shown to decrease mortality; however, adherence to an LCS program remains significantly lower than in randomized controlled trials.
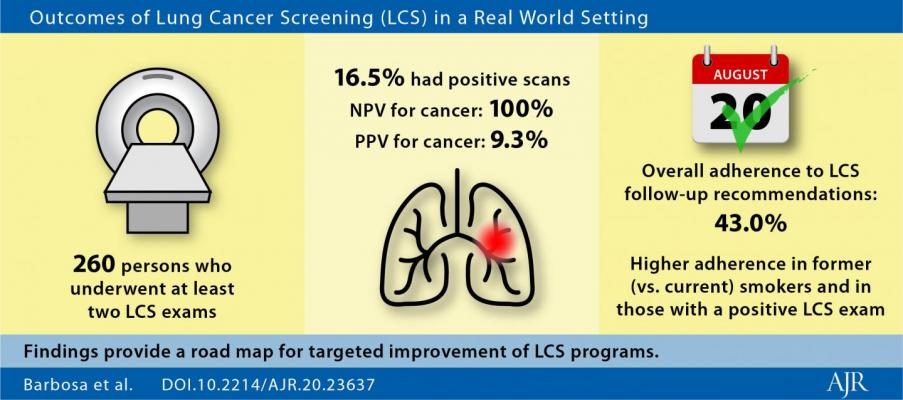
To assess real-world LDCT LCS performance and factors predictive of adherence to recommendations, three radiologists from the University of Pennsylvania's Perelman School of Medicine retrospectively recorded patient demographics, smoking history and behavior changes, Lung-RADS category, PPV and NPV, and adherence to screening recommendations for 260 subjects returning for follow-up LDCT from 2014 to 2019.
Forty-three subjects (16.5%) had positive scans, of which 28/260 (10.8%) were Lung-RADS category 3, 8/260 (3.1%) were 4A, 6/260 (2.3%) were 4B, and 2/260 (0.8%) were 4X.
Four subjects were diagnosed with cancer: 3 lung, 1 metastatic melanoma.
Meanwhile, 143/260 (55%) subjects were current smokers at baseline, and 121/260 (46.5%) were current smokers during the last round of LCS.
Both LCS sensitivity and NPV were 100%, while specificity was 84.8% and PPV was 9.3%.
Overall adherence was 43%, though it increased progressively the higher the Lung-RADS category. Additionally, adherence was higher in former vs. current smokers (50% vs. 36.2%; p = 0.002). Ultimately, there were only two significant independent predictors of adherence: having smoked previously and a positive (? 3) Lung-RADS category.
"Our study demonstrates that a real-world LCS can perform similar to randomized controlled trials in regard to important performance metrics," concluded first author Eduardo J. Mortani Barbosa, Jr.
Acknowledging that an economic incentive, such as an insurance premium reduction, could improve LCS adherence, Barbosa, Jr. et al. added that multimodal communication (i.e., face-to-face discussions with radiologists, letters from referring providers, reminders via electronic health records) should be investigated and incentivized.
"Such communications should emphasize that a negative LCS exam does not confer immunity to future lung cancer development," the authors of this AJR article noted, "and that continued participation in LCS, combined with smoking cessation, is essential to accrue the maximum benefits of mortality reduction amongst persons with substantial smoking history."
For more information: www.


 March 12, 2026
March 12, 2026