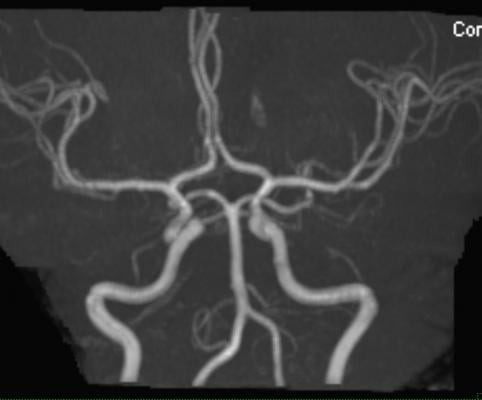
June 8, 2018 — Whole-body magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) found a surprisingly high prevalence of atherosclerosis in people considered at low to intermediate risk for cardiovascular disease, according to a study appearing online in the journal Radiology. Almost half of all study participants had at least one narrowed artery.
Atherosclerotic disease is characterized by a narrowing of the arteries caused by plaque buildup. The condition often progresses to cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death in the United States. Early intervention can slow or reverse disease progression, but standard imaging techniques for early detection focus on specific artery segments, potentially missing evidence of disease elsewhere in the body.
Whole-body MRA allows clinicians to take a broader view of the vascular system.
“The key advantages of this MRA technique include the ‘whole-body’ approach, which detects systemic disease that would be missed by modalities assessing single vascular sites,” said study co-author Graeme Houston, M.D., from the University of Dundee in Dundee, Scotland. “The results offer a validated quantitative score of atherosclerotic burden, and the technique does not use ionizing radiation, which is an advantage over CT [computed tomography] angiography.”
Houston and colleagues used whole-body MRA to quantify the burden and distribution of asymptomatic atherosclerosis in 1,513 people, average age 53.5 years old. The participants were considered in the low-intermediate risk group, with a 10-year cardiovascular disease risk of less than 20 percent. The researchers assessed 31 arterial segments in each participant.
The plaque burden, or overall amount of atherosclerotic plaque, and number of narrowed vessels correlated with age, blood pressure and cholesterol — all known risk factors for cardiovascular events like heart attacks. But the prevalence of atherosclerosis in the study group was surprisingly high. Almost half of the participants had at least one narrowed vessel, and more than a quarter had multiple narrowed vessels.
“This is surprising, given that the study group was made up of asymptomatic individuals without diabetes who had low to intermediate risk of future cardiovascular events by standard risk factor assessment,” Houston said.
With whole-body MRA, the researchers were able to detect early atherosclerotic disease throughout the body, disease that would have been missed by methods that evaluate only a single vascular territory. The technique’s high technical success rate — researchers were able to interpret 99.4 percent of the potentially analyzable arterial segments — underscores its potential for more widespread use.
“The results confirm the feasibility for MRA as an imaging method for detecting early atherosclerotic disease in individuals at low- to intermediate-risk of cardiovascular events,” Houston said. “This approach could stratify individuals for the presence of disease burden, which could inform further preventative therapy in the future.”
The researchers plan to conduct follow-up studies to look for links between whole-body MRA findings and long-term health outcomes.
For more information: www.pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology
Reference


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026