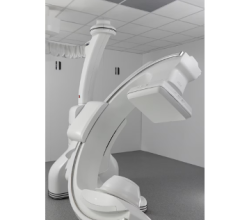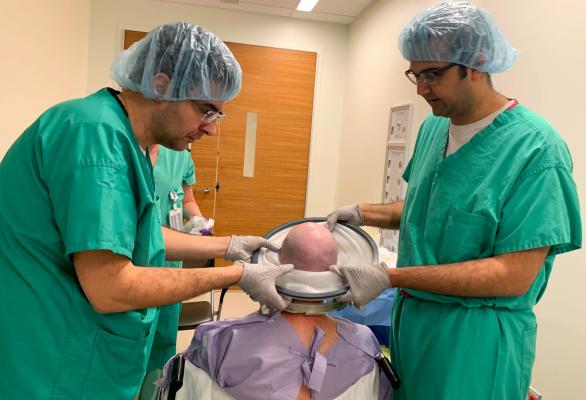
Vibhor Krishna, M.D., (right) fits David Shorr with a helmet-like device used in a new clinical trial for Alzheimer’s disease at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. The device uses MRI-guided imaging to deliver focused ultrasound to specific areas of the brain to open the blood-brain barrier. Image courtesy of Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center.
May 9, 2019 — A new clinical trial at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and two other sites is testing an innovative procedure that may provide hope in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease.
The non-invasive procedure uses low-intensity focused ultrasound to open the blood-brain barrier, a protective layer that shields the brain from infections or pathogens in the blood. However, this barrier also makes it nearly impossible to deliver therapeutics to the brain to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
“While it’s protective and beneficial for day-to-day brain function, when we think about therapeutics, the blood-brain barrier poses a significant challenge,” said Vibhor Krishna, M.D., a neurosurgeon at Ohio State Wexner Medical Center. “The focused ultrasound procedure allows us to non-invasively access the brain tissue so treatment can be administered straight to the site of pathology.”
During the surgery in an intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-surgical suite, patient David Shorr of Bexley, Ohio, was awake and alert, giving real-time feedback to the treatment team of neurosurgeon, neurologist, neuropsychologist, researchers and nurses.
MRI-guided imaging allows doctors to target a specific area of the brain where there is a buildup of toxic proteins called amyloid. A head frame holds the patient’s head still during the treatment. The ultrasound transducer — essentially a helmet housing the ultrasound beams — is attached to the head frame. Surrounding the patient’s head is a water bath where cold, degassed water is circulated. This setup helps transmission of 1,000 focused ultrasound beams from the machine through intact skull, all converging at the exact brain tissue that is being targeted.
During the procedure, the patient’s bloodstream is infused with microbubbles. The focused ultrasound waves are delivered through the helmet-like device, which causes microbubbles in the blood to oscillate and open the blood-brain barrier.
“In this research study, we are not delivering any medications. Our hypothesis is that, by opening the blood brain barrier, a patient’s own immune defense may clear some of those harmful amyloids,” Krishna said. “If we determine this to be safe, in the next steps we would want to understand the effectiveness and the impact of opening the blood-brain barrier in improving cognitive decline.”
The procedure is performed three times at two-week intervals to allow for as much amyloid clearance as possible. In the future, this method of opening the blood-brain barrier may also be applicable in developing new treatments for brain tumors and epilepsy.
“With 5.8 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s, there’s a critical need to develop novel therapies to treat this devastating disease. With this innovative clinical trial, Ohio State researchers are pioneering potential new treatments,” said K. Craig Kent, M.D., dean of the Ohio State University College of Medicine.
The research team at Ohio State’s Center for Neuromodulation will monitor the patients closely, using neurological exams and neuro-psychological exams to assess language, memory and executive functioning at various intervals for one year following the surgery.
The clinical trial, sponsored by Insightec, will enroll up to 10 patients at Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Weill Cornell Medicine and West Virginia University Rockefeller Neuroscience Center.
“We’re hopeful it can help him, but we also know maybe it will help somebody else,” said Shorr’s wife, Kim.
For more information: www.wexnermedical.osu.edu


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026