January 23, 2024 — Siemens Healthineers announces the …
PET-MRI
PET-MRI combines positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) into one imaging system. Positron emission tomography–magnetic resonance imaging (PET-MRI) is a hybrid imaging technology that incorporates magnetic resonance imaging soft tissue morphological imaging and positron emission tomography functional imaging.
Feb. 27, 2026 — NYC Health + Hospitals/Jacobi | North Central Bronx recently unveiled a new $2 million MRI suite at the ...
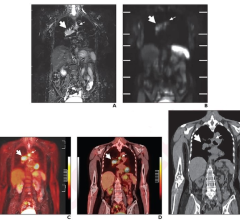
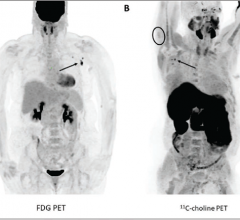
July 31, 2024 — In a head-to-head comparison with FDG PET/CT, FDG PET/MRI demonstrated comparable or superior diagnostic ...
January 23, 2024 — Siemens Healthineers announces the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance of syngo Virtual ...
People who live in rural America may deserve the same quality healthcare as anyone living in the U.S., but it is not ...
December 1, 2023 — In today's healthcare environment, the industry faces various pressing challenges. The magnetic ...
November 30, 2023 — Through its leading imaging solutions and commitment to innovation, GE HealthCare remains at the ...
June 28, 2023 — GE HealthCare is set to unveil SIGNA PET/MR AIR[i], at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular ...
March 29, 2023 — In a partnership which aims to provide faster and safer medical imaging across Australia and New ...
March 10, 2023 — Researchers found evidence of heart muscle inflammation in a small number of patients with acute ...
June 22, 2022 — Andrei Iagaru, MD, FACNM, professor of radiology (nuclear medicine) and chief of the Division of Nuclear ...
June 21, 2022 — Markus Schwaiger, MD, a scientist known for his contributions to cardiac PET imaging, has been named as ...
May 10, 2022 — At the ISMRM 2022 conference, Bruker announced the launch of innovative 7 Tesla and 9.4 Tesla conduction ...
January 17, 2022 — The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) issued a statement on Jan. 14 regarding ...
December 29, 2021 — The global nuclear imaging devices and equipment market is expected to grow from $2.45 billion in ...
December 10, 2021 — According to an article in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), MRI—with or without FDG ...
The use of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in preclinical oncology investigations has shown the ability to ...
August 27, 2021 — The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) issued two cooperative ...
August 2, 2021 — The global molecular imaging market was evaluated at $4.199 billion for the year 2019 growing at a CAGR ...
July 21, 2021 — Registration is now open for the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) 107th Scientific Assembly ...
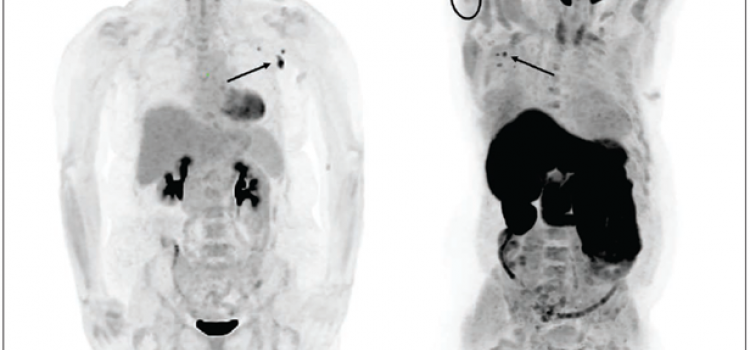
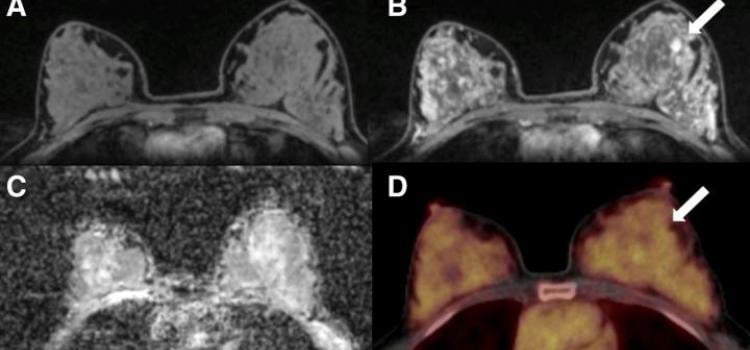
May 19, 2021 — According to an open-access article in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), increased axillary ...
May 5, 2021 — For patients with brain metastases, amino acid positron emission tomography (PET) can provide valuable ...




 March 05, 2026
March 05, 2026