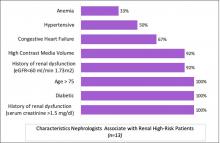
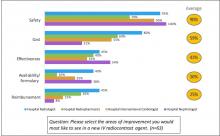
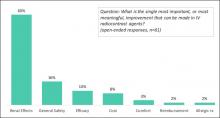
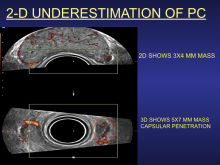
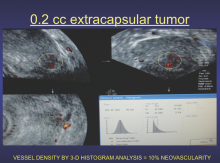
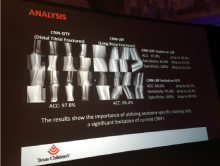
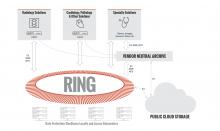
September 5, 2019 — An ahead-of-print article published in the December issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) provides a primer of gender affirmation surgical therapies encountered in diagnostic imaging.[1] The article defines normal post-surgical anatomy and describes select complications using a multidisciplinary, multimodality approach.
© Copyright Wainscot Media. All Rights Reserved.
Subscribe Now