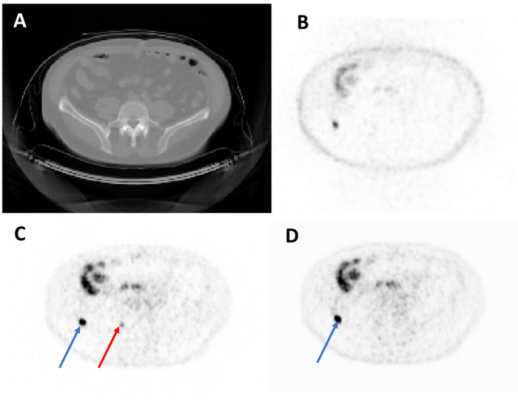
Representative axial image from a test set imaging study. From top left to bottom right: CT (A), NAC-PET (B), original AC-PET (C), AI-generated AC-PET (D). The blue arrow indicates one lesion that was observed in both images, and the red arrow indicates a lesion that was missed (i.e., not de-tected by expert nuclear medicine physicians) in AI image. NAC = Non-Attenuation Corrected. AC = Attenuation-Corrected. Image courtesy of Kevin Ma, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, College Park, Maryland; Esther Mena, Liza Lindenberg, Deborah Citrin, William Dahut, James Gulley, Peter Choyke, Baris Turkbey, and Stephanie Harmon, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; Peter Pinto, Urologic Oncology Branch, National Cancer Insititute, National Insitutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; Bradford Wood, Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; and Ravi Madan, Genitourinary Malignancies Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland.
June 14, 2022 — A novel artificial intelligence method can be used to generate high-quality “PET/CT” images and subsequently decrease radiation exposure to the patient. Developed by the National Cancer Institute, the method bypasses the need for CT-based attenuation correction, potentially allowing for more frequent PET imaging to monitor disease and treatment progression without radiation exposure from CT acquisition. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2022 Annual Meeting.
Cancer patients often undergo several imaging studies throughout diagnosis and treatment, potentially including multiple PET/CT scans in close succession. The CT portion of the exam contributes to a patient’s overall radiation exposure yet is largely redundant. In this study, researchers sought to reduce or eliminate the need for low-dose CT in PET/CT by using an artificial intelligence model to generate virtual attenuation-corrected PET scans.
The data cohort for artificial intelligence model development included 305 18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT studies. Each study contained three scans: non-attenuation-corrected PET, attenuation-corrected PET, and low-dose CT. Studies were broken down into three sets for training (185), validation (60) and testing (60). A 2D Pix2Pix generator was then used to generate synthetic attenuation-corrected PET scans (gen-PET) from the original non-attenuation-corrected PET.
For qualitative evaluation, two nuclear medicine physicians reviewed 40 PET/CT studies in a randomized order, blinded to whether the image was from original attenuation-corrected PET or gen-PET. Each expert recorded the number and locations of PET-positive lesions and qualitatively reviewed overall noise and image quality. The readers were able to successfully detect lesions on the gen-PET images with reasonable sensitivity values.
“High-quality artificial intelligence-generated images preserve vital information from raw PET images without the additional radiation exposure from CT scans,” said Kevin Ma, PhD, a post-doctoral researcher at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Maryland. “This opens opportunities for increasing the frequency and number of PET scans per patient per year, which could provide more accurate assessment for lesion detection, treatment efficacy, radiotracer effectivity, and other measures in research and patient care.”
Abstract 151. “Artificial Intelligence-generated PET images for PSMA-PET/CT studies: Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment,” Kevin Ma, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, College Park, Maryland; Esther Mena, Liza Lindenberg, Deborah Citrin, William Dahut, James Gulley, Peter Choyke, Baris Turkbey, and Stephanie Harmon, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; Peter Pinto, Urologic Oncology Branch, National Cancer Insititute, National Insitutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; Bradford Wood, Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland; and Ravi Madan, Genitourinary Malignancies Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland.
For more information: www.snmmi.org

 March 09, 2026
March 09, 2026 









