
16-year-old girl with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and known history of tuberous sclerosis who presented with acute hypoxic respiratory distress. Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction testing confirmed diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
A, Frontal chest radiograph obtained at initial presentation shows bilateral lower lung zone–predominant consolidations and, to lesser extent, ground-glass opacities. B, Frontal chest radiograph obtained 2 days after hospital admission shows interval increase in consolidation in bilateral lower lung zones. C, Frontal chest radiograph obtained 6 days after hospital admission and treatment shows interval improvement in consolidations in bilateral lower lung zones.
May 1, 2020 — Although the clinical symptoms of new pediatric lung disorders such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), swine-origin influenza A (H1N1), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI), and coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia may be nonspecific, some characteristic imaging findings “have emerged or are currently emerging,” according to an open-access article in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
“Although there are some overlapping imaging features of these disorders,” wrote first author Alexandra M. Foust of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, “careful evaluation of the distribution, lung zone preference, and symmetry of the abnormalities with an eye for a few unique differentiating imaging features, such as the halo sign seen in COVID-19 and subpleural sparing and the atoll sign seen in EVALI, can allow the radiologist to offer a narrower differential diagnosis in pediatric patients, leading to optimal patient care.”
At most institutions, whereas the first imaging study performed in patients with clinically suspected COVID-19 is chest radiography, Foust and colleagues’ review of the clinical literature found that studies on chest radiography findings in patients with COVID-19 were relatively scarce.
Regarding the limited studies of pediatric patients with COVID-19, Foust et al. noted chest radiography “may show normal findings; patchy bilateral ground-glass opacity (GGO), consolidation, or both; peripheral and lower lung zone predominance.”
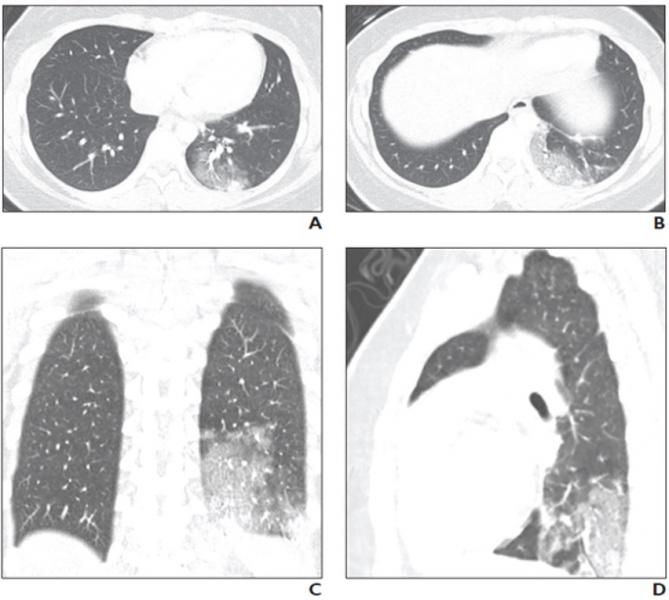
Similarly, while the literature describing chest computed tomography (CT) findings in patients with COVID-19 are more robust than those describing chest radiography findings, only a few articles have reported CT findings of COVID-19 in children.
A study of 20 pediatric patients with COVID-19 reported that the most frequently observed abnormalities on CT were subpleural lesions (100% of patients), unilateral (30%) or bilateral (50%) pulmonary lesions, GGO (60%), and consolidation with a rim of GGO surrounding it, also known as the halo sign (50%).
The authors of this AJR article also pointed to a smaller study of five pediatric patients with COVID-19, where investigators reported modest patchy GGO, one with peripheral subpleural involvement, in three patients that resolved on follow-up CT examination.
For more information: www.arrs.org
Related Coronavirus Content:
VIDEO: Imaging COVID-19 With Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
The Cardiac Implications of Novel Coronavirus
CT Provides Best Diagnosis for Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Radiology Lessons for Coronavirus From the SARS and MERS Epidemics
Deployment of Health IT in China’s Fight Against the COVID-19 Epidemic
Emerging Technologies Proving Value in Chinese Coronavirus Fight
Radiologists Describe Coronavirus CT Imaging Features
Coronavirus Update from the FDA
CT Imaging of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Pneumonia
CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
Chest CT Findings of Patients Infected With Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV Pneumonia
Find more related clinical content Coronavirus (COVID-19)
ACC COVID-19 recommendations for the cardiovascular care team
VIDEO: What Cardiologists Need to Know about COVID-19 — Interview with Thomas Maddox, M.D.
The Cardiac Implications of Novel Coronavirus
ESC Council on Hypertension Says ACE-I and ARBs Do Not Increase COVID-19 Mortality


 March 11, 2026
March 11, 2026 









