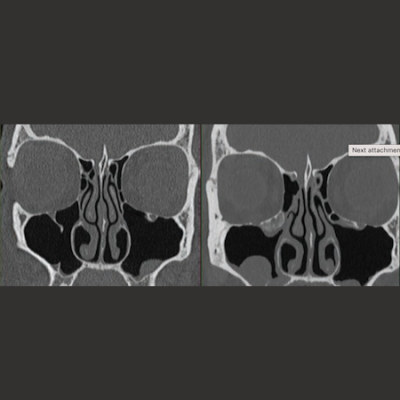
Coronal images are shown. PCD examination included additional dose reduction methods including tin filtration and ultrahigh-resolution acquisition. CTDIvol is lower for PCD than for EID scanner (9 vs 26 mGy, respectively); yet, PCD-CT image has less noise. EID CT examination was performed on Siemens Sensation 64 scanner with following parameters: detector configuration, 32x0.6 mm; z-flying focal spot (64x0.6 mm); tube potential, 120 kV; rotation time, 1 second; helical pitch, 0.9; effective mAs, 170; kernel, H70; slice thickness, 0.75 mm; matrix, 512. PCD-CT examination was performed on Siemens NAEOTOM Alpha scanner with following parameters: detector configuration, 120x0.2 mm; tube voltage, 100 kV with added tin filter; rotation time, 1 second; helical pitch, 0.85; kernel, Hr72 with QIR strength setting of 3; slice thickness, 0.6; mm; matrix, 1024. (Photo: American Roentgen Ray Society)
Feb. 4, 2026 — A new review published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) finds that advances in CT technology over the past 25 years have enabled routine radiation dose reductions by a factor of 2 to 10, while preserving diagnostic performance when applied appropriately.
Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, and Lifeng Yu, PhD, of Mayo Clinic Minnesota traced major milestones in CT dose reduction since the early 2000s, highlighting the cumulative impact of hardware innovations, scanning technique optimization and advances in image reconstruction algorithms.
According to Drs. McCollough and Yu, the introduction of photon-counting detector (PCD) CT represents a major leap forward in dose efficiency. PCD CT improves signal quality by rejecting electronic noise, optimizing photon-energy weighting, and enabling ultrahigh-resolution acquisitions without proportional dose penalties.
Importantly, this AJR review cautions that dose reduction alone is not a sufficient metric of progress. The authors emphasize that diagnostic performance must be preserved through objective, task-based image quality assessment, particularly as deep learning–based reconstruction and postprocessing tools are increasingly deployed in clinical practice.
Using historical and contemporary CT examples, McCollough and Yu demonstrate that modern scanners can achieve image quality equal to or superior to that of legacy systems at a fraction of the radiation dose, especially when advances are applied in combination and tailored to specific clinical tasks.
The authors conclude that continued progress in CT dose reduction will depend on close collaboration among radiologists, technologists, and medical physicists, as well as careful validation of emerging technologies to ensure patient safety without compromising diagnostic accuracy.
Watch Dr. McCollough discuss her article reviewing key milestones and technologic innovations that have led to this substantial reduction in CT radiation doses—providing examples of the cumulative impact of these advances on image quality for routine examinations in various anatomic sites.


 March 12, 2026
March 12, 2026