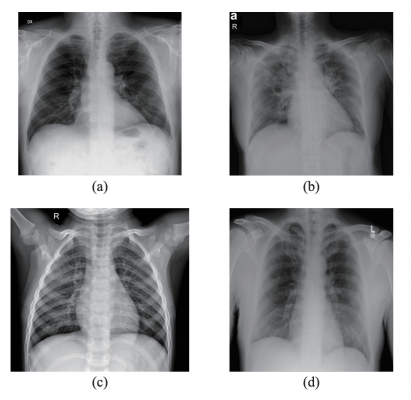
Samples from the dataset used in this study. (a) X-ray with PA view of a patient with COVID-19; (b) X-ray with AP view of a patient with COVID-19; (c) X-ray of a healthy patient from Dataset A; (d) X-ray of a healthy patient from Dataset B. Images courtesy of IEEE/CAA JOURNAL OF AUTOMATICA SINICA
March 29, 2021 — X-rays, first used clinically in the late 1890s, could be a leading-edge diagnostic tool for COVID-19 patients with the help of artificial intelligence, according to a team of researchers in Brazil who taught a computer program, through various machine learning methods, to detect COVID-19 in chest X-rays with 95.6 to 98.5% accuracy.
They published their results in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
The researchers have previously focused on detecting and classifying lung pathologies, such as fibrosis, emphysema and lung nodules, through medical imaging. Common symptoms presented by suspected COVID-19 infections include respiratory distress, cough and, in more aggressive cases, pneumonia - all visible via medical imaging such as computed tomography (CT) scans or X-rays.
"When the COVID-19 pandemic arose, we agreed to put our expertise to use to help deal with this new global problem," said corresponding author Victor Hugo C. de Albuquerque, a researcher in the Laboratory of Image Processing, Signals, and Applied Computing and with the Universidade de Fortaleza.
Many medical facilities have both an inadequate number of tests and lengthy processing times, Albuquerque said, so the research team focused on improving a tool that is readily available at every hospital and already frequently used in diagnosing COVID-19: X-ray devices.
"We decided to investigate if a COVID-19 infection could be automatically detected using X-ray images," Albuquerque said, noting that most X-ray images are available within minutes, compared to the days required for swab or saliva diagnostic tests.
However, the researchers found a lack of publicly available chest X-rays to train their artificial intelligence model to automatically identify the lungs of COVID-19 patients. They had just 194 COVID-19 X-rays and 194 healthy X-rays, while it usually takes thousands of images to thoroughly teach a model to detect and classify a particular target. To compensate, they took a model trained on a large dataset of other X-ray images and trained it to use the same methods to detect lungs likely infected with COVID-19. They used several different machine learning methods, two of which resulted in a 95.6% and a 98.5% accuracy rating, respectively.
"Since X-rays are very fast and cheap, they can help to triage patients in places where the health care system has collapsed or in places that are far from major centers with access to more complex technologies," Albuquerque said. "This approach to detect and classify medical images automatically can assist doctors in identifying, measuring the severity and classifying the disease."
Next, Albuquerque said, the researchers plan to continue testing their method with larger datasets as they become available, with the ultimate goal of developing a free online platform for medical image classification.
For more information: www.


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









