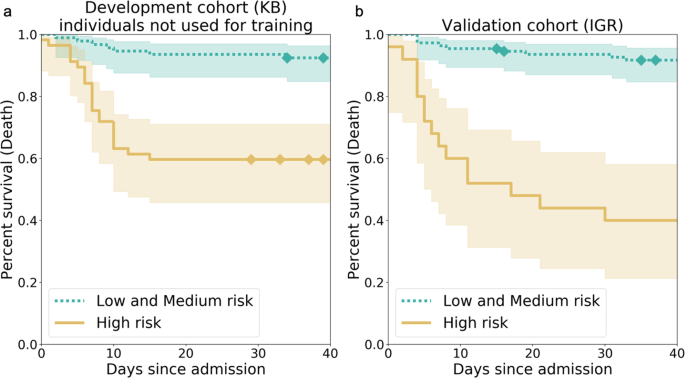
Kaplan–Meier curves for the high-risk individuals and the ones with low or medium risk according to AI-severity. The threshold to assign individuals into a high-risk group was the 2/3 quantile of the AI-severity score computed for patients of the KB development cohort. a Kaplan–Meier curves were obtained for the 150 leftover KB patients from the development cohort. b Kaplan–Meier curves were obtained for the 135 patients of the IGR validation cohort. p-values for the log-rank test were equal to 4.77e–07 (KB) and 4.00e–12 (IGR). The two terciles used to determine threshold values for low-, medium-, and high-risk groups were equal to 0.187 and 0.375. Diamonds correspond to censoring of patients who were still hospitalized at the time when data ceased to be updated. The bands correspond to the sequence of the 95% confidence intervals of the survival probabilities for each day. KB Kremlin-Bicêtre hospital, IGR Institut Gustave Roussy hospital. Courtesy of Nature Communications.
February 1, 2021 — COVID-19 vaccine distribution has begun across the globe, while many countries are still struggling with the rampant rise of infections. Owkin, a French-American startup pioneering artificial intelligence (AI) and Federated Learning in medical research, has been focusing its COVID-19 research efforts on aspects of the pandemic that still require much public health attention, despite the arrival of an effective vaccine.
Efforts to support frontline health systems as they devote their resources to the influx of COVID-19 related hospitalizations, have resulted in the AI-Severity Score, published in Nature Communications. This machine learning model, trained on multimodal data sets that include computed tomography (CT) scans of the lungs (a routine procedure upon admission), is plug and play and able to predict the severity of a patient's disease prognosis with a performance that surpasses all other currently published score benchmarks. Use of these scores supports hospital resource management and planning, a sometimes overlooked function that, when managed well, saves lives. This research was made possible through a consortium, called ScanCovIA, made up of Institut Gustave Roussy, Kremlin-Bicêtre APHP, Owkin, and Digital Vision Center of CentraleSupélec and INRIA.
Additionally, Owkin has been developing other machine learning models to discover more coronavirus epitopes that are most likely to be effective in future vaccines As the virus continues to mutate, we don't yet know how long the current vaccines will remain efficacious or if, like the flu, they will require annual or semi annual development. Furthermore, it may be possible to develop vaccines for genes within the virus's DNA that are more stable, and less likely to mutate. Epitope prediction can speed vaccine development by narrowing the field of epitopes to test in the lab, and it can diversify our defenses against the virus's future mutations. Furthermore, these models can be deployed outside vaccine research; they can also be used in oncology research. The ultimate aim of machine learning for epitope discovery is to have a better understanding of the immune response--these features of the model have their place across the spectrum of precision medicine research.
For more information: www.


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









