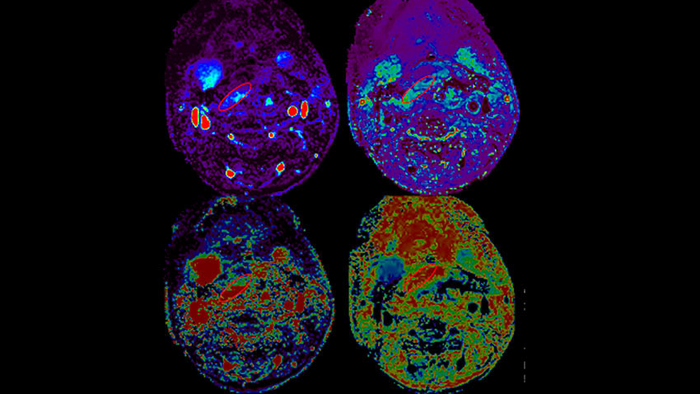
A composite picture from MR perfusion of a free flap demonstrating measurements made within the flap. Image courtesy of Michigan Medicine
June 30, 2022 — When a patient with head and neck cancer has surgery to remove it, they often need reconstructive surgery in the form of a “free flap”, which is skin and tissue taken from a different part of the body and connected to the blood vessels of the wound in need of repair.
This free flap method, called microvascular reconstruction, carries around a 10-40% risk of wound complications, with 10% of cases requiring another surgery. A Michigan Medicine study finds that early postoperative CT scans and MRIs can help predict whether a flap will fail, which could allow surgeons to intervene earlier. The results are published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology.
“All patients who have this procedure can be investigated with non-invasive post-operative CT or MRI perfusion, and these two methods show a lot of promise as accurate biomarkers of predicting free flap viability,” said Ashok Srinivasan, M.D., FACR, senior author of the paper and neuroradiologist at University of Michigan Health.
“By seeing how much blood is flowing in and out of the tissue, we may be able to predict if the flap will succeed and if the patient can be discharged earlier, or it may be able to tell us sooner that surgical intervention is needed to repair the flap. Radiologists have used CT and MRI perfusion with contrast to look at blood perfusion in brain imaging for a stroke or tumor, but no studies have used them to look at free flaps early after a procedure.”
The U-M Head and Neck Oncology Program performs approximately 300 free flaps a year, with each of these patients staying approximately one week in the hospital after surgery. The ability to predict which patients are safe for an earlier discharge would have significant and immediate cost savings, says Matthew Spector, M.D., co-author of the paper and otolaryngologist at U-M Health.
Currently, most surgeons use ultrasound to assess viability for free flap reconstruction with techniques known as doppler and skin paddle. Those methods often are unable to evaluate deeper aspects of the flap, or air and blood products cause interference in visualization, which affects how well clinicians can analyze a flap’s viability, says Srinivasan, who is also a clinical professor of radiology at U-M Medical School.
The team of researchers analyzed 19 patients who had successful free flap reconstruction, as well as five who had wound failure, at U-M Health between January 2016 to mid-2018. They found that both CT and MRI perfusion techniques showed significant differences between the two patient groups.
Researchers were not able to compare the two methods to ultrasound techniques or each other due to the small sample size. They hope to accomplish those comparisons through a larger future trial.
“This pilot research shows us that these models work, as all areas of the flap can be assessed using CT and MRI, unlike doppler and skin paddle where some areas may be blind to evaluation,” said Yoshiaki Ota, M.D., lead author of the paper and a neuroradiology fellow at University of Michigan Health. “We know that using CT and MRI could help shorten a patient’s hospital stay or avoid a prolonged hospitalization, and now we need to look further at which is more effective and cost-effective.”
Additional authors include: Keith Casper, M.D., Chaz Stucken, M.D., Kelly Malloy, M.D., Remy Lobo, M.D., Akira Baba, M.D., Ph.D., all of Michigan Medicine, and Andreea Moore, M.D., Western Michigan University School of Medicine.
This work received funding from the American Society of Head and Neck Radiology under the William N. Hanafee, M.D., Research Grant and from the Internal Seed Grant of the Department of Radiology at the University of Michigan.
For more information: https://med.umich.edu/


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026