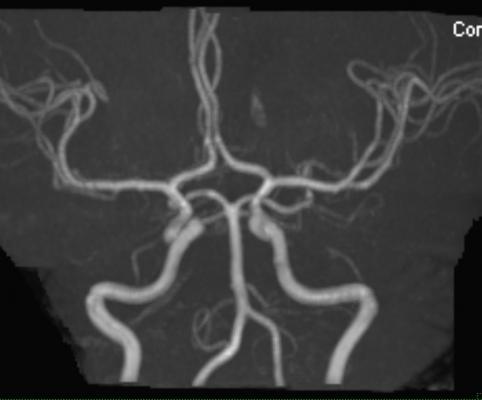
April 29, 2016 — Bayer announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Gadavist (gadobutrol) injection for use with magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to evaluate known or suspected supra-aortic or renal artery disease. The injection was approved for use in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates).
The FDA approval is based on the results of two multi-center, Phase 3, open-label clinical studies – the GEMSAV study of patients with known or suspected vascular disease of the supra-aortic arteries, and the GRAMS study of patients with known or suspected renal artery disease.
“Until now, no contrast agents were FDA-approved for use with MRA of the supra-aortic arteries," said Elias Melhem, M.D., chair, Department of Diagnostic Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland, and principal investigator for the GEMSAV study. “With FDA's action, radiologists now have an approved MRA contrast agent to help visualize supra-aortic arteries in patients with known or suspected supra-aortic arterial disease, including conditions such as prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).”
In the studies, gadobutrol met the primary objective of superior assessability (ability to see more vessel segments) and non-inferior sensitivity and specificity as compared to non-contrast MRA. Gadobutrol-enhanced MRA demonstrated statistically significant higher assessability (visualization) versus non-contrast MRA images.
The GEMSAV (Gadavist-Enhanced MRA of the Supra-Aortic Vessels) study evaluated 457 patients with known or suspected disease of the supra-aortic arteries. Efficacy was evaluated based on visualization and performance for distinguishing between normal and abnormal anatomy. Significant stenosis was defined as at least 70 percent.
Key findings of this open-label Phase 3 study, in which Gadavist was delivered at 1.5mL/second, include:
- Gadavist MRA significantly improved visualization, or assessability, (range across three readers: 88-97 percent) as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 24-82 percent);
- Gadavist MRA specificity for exclusion of clinically significant disease (range across three readers: 92-97 percent) showed non-inferiority as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 62-89 percent);
- Gadavist MRA sensitivity (range across three readers: 58-60 percent) showed non- inferiority as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 54-55 percent); and
- Low sensitivity for significant arterial stenosis. For all three supra-aortic artery readers, the lower bound of confidence for the sensitivity of Gadavist MRA for detecting arterial segments with significant stenosis did not exceed 54 percent. A negative MRA alone should not rule out significant stenosis.
The GRAMS (Gadavist-Enhanced Renal Artery MRA) study evaluated 292 patients with known or suspected disease of the renal arteries. Efficacy was evaluated based on visualization and performance for distinguishing between normal and abnormal anatomy. Significant stenosis was defined as at least 50 percent.
Key findings of this open-label Phase 3 study, in which Gadavist was delivered at 1.5mL/second, include:
- Gadavist MRA significantly improved visualization, or assessability, (range across three readers: 96-98 percent) as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 72-82 percent);
- Gadavist MRA specificity for exclusion of clinically significant disease (range across three readers: 94-95 percent) showed non-inferiority as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 81-85 percent);
- Gadavist MRA sensitivity (range across three readers: 52-54 percent) showed non-inferiority as compared to unenhanced MRA (range across three readers: 39-51 percent);
- Low sensitivity for significant arterial stenosis. For all three renal artery readers, the lower bound of confidence for the sensitivity of Gadavist MRA for detecting arterial segments with significant stenosis did not exceed 46 percent. A negative MRA alone should not rule out significant stenosis; and
- Gadavist MRA improved visualization of accessory renal arteries for surgical planning and renal donor evaluation as compared to unenhanced MRA.
Finally, overall the safety results from the two Phase 3 MRA studies in patients with known or suspected arterial disease are consistent with the safety data observed in clinical trials in more than 6,000 subjects. The results support the benefit-risk profile of Gadavist for appropriate patients.
These studies are planned to be presented at medical meetings later this spring.
For more information: www.healthcare.bayer.com


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026