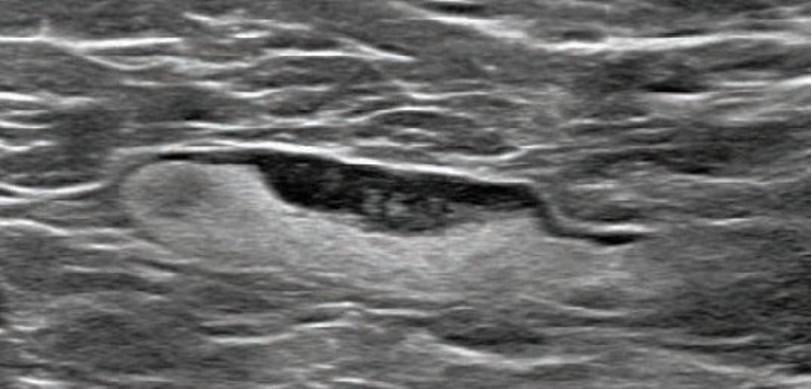
55-year-old woman who underwent screening mammogram and ultrasound 7 days after first COVID-19 vaccination dose. Screening mammogram and US demonstrated unilateral left axillary lymph node with cortical thickness of 5 mm on ultrasound (not shown). BI-RADS category 0 was assigned. Ultrasound from diagnostic work-up performed 7 days later showed no change in lymph node size. BI-RADS 3 was assigned.
February 24, 2021 — An open-access article in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) describes the clinical and imaging features of axillary adenopathy detected during screening or diagnostic breast imaging after recent coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination to inform the development of follow-up recommendations.[1]
Adenopathy is inflammation that involves glandular tissue or lymph nodes. This study shows the presence of swollen lymph nodes on mammograms of women who have received the COVID-19 vaccines and suggests patients should be asked if they recently received the vaccine.
Shabnam Mortazavi, M.D., of the University of California at Los Angeles reviewed electronic medical records to identify women with post-COVID-19 vaccination adenopathy found from December 2020 to February 2021. For mammography, Mortazavi considered a node abnormal when its size, shape, or density was deemed disproportionate to other axillary nodes (ipsilateral or contralateral). On ultrasound, she deemed a node abnormal based on subjective assessment for cortical abnormalities, including focal or diffuse thickening greater than 3 mm, as well as nodal prominence compared to the contralateral axilla (when available). For MRI, Mortazavi considered a node abnormal when asymmetric in size and/or number to the contralateral axilla.
Twenty-three women exhibited axillary adenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccinated arm on screening or diagnostic breast imaging, and according to Mortazavi, “13% were symptomatic (axillary lump with possible tenderness).” Meanwhile, the adenopathy was detected incidentally on screening breast imaging in 43% (mammography, 5; ultrasound, 2; both mammography and ultrasound, 1; high-risk screening MRI, 2) and on diagnostic imaging for other reasons in 43% (BI-RADS 3 follow-up for breast finding, 3; screening callback for other reason, 2; non-axillary breast pain or lump, 5). Noting that the median interval between the first vaccine dose and imaging showing the abnormal node was 9.5 days, Mortazavi’s results counted a total of 57% of women with one abnormal node. BI-RADS 2 was assigned in one woman, BI-RADS 3 in 21 (ultrasound in 4–24 weeks), and BI-RADS 4 in one.
“The largest sample to our knowledge of COVID-19 vaccine associated axillary adenopathy on imaging,” Mortazavi also wrote, “this study highlights axillary adenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccinated arm with Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccine as a potential reactive process with which radiologists must be familiar.” Ultimately, vaccination date and laterality are critical to optimize assessment and management of imaging-detected axillary adenopathy in women with otherwise normal breast imaging.
For more information: www.arrs.org
VIDEO: COVID Vaccine May Cause Enlarged Lymph Nodes on Mammograms — Interview with Constance "Connie" Lehman, M.D., Mass General Hospital
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
CMS Now Requires COVID-19 Vaccinations for Healthcare Workers by January 4
Find more radiology related COVID content
Reference:


 March 09, 2026
March 09, 2026 









