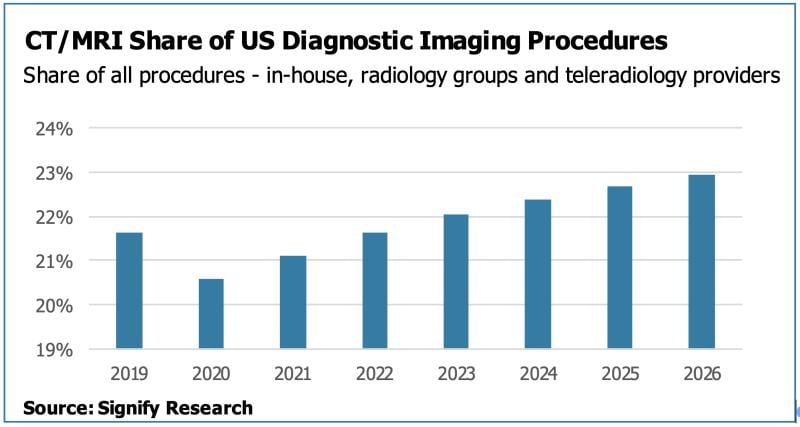
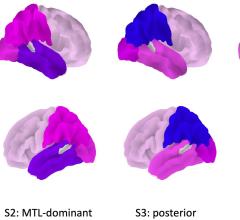
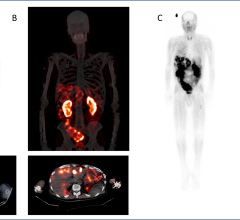
July 12, 2023 — United Imaging, a global leader in manufacturing advanced medical imaging and radiotherapy equipment and ...
Molecular Imaging
Nuclear imaging, also called molecular imaging, includes positron emission computed tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging. This section includes radiopharmaceuticals and tracers, PET-CT, SPECT-CT, and PET-MRI. Molecular imaging includes the field of nuclear medicine, which uses very small amounts of radioactive materials, or radiopharmaceuticals, to diagnose and treat disease.
The healthcare market is witnessing a dynamic shift in how and where patients want to receive care, with the flexibility ...
July 11, 2023 — Ratio Therapeutics Inc. (Ratio), a pharmaceutical company that employs a suite of innovative ...
Technological advancements in positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) offer both clinicians and ...
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is cheaper, easier to use and its results are easier to understand than ...
July 5, 2023 — NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes, LLC, a global innovator in the development, production and ...
July 3, 2023 — RefleXion Medical, Inc., a therapeutic oncology company, today announced that results of a prospective ...
Efficiency and effectiveness are inseparable in clinical medicine. Digital PET addresses them both. The key is the ...
June 30, 2023 — The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) hosted nearly 8,000 physicians ...
June 29, 2023 — Research presented at the 2023 Annual Meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging ...
June 29, 2023 — A study presented this week during the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) ...
Introducing HYPERSCAN , Pencil Beam Scanning Delivery HYPERSCAN enables tumor volumes to be scanned in a matter of ...
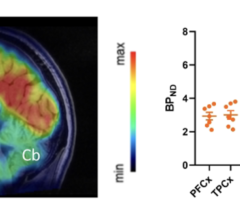
June 28, 2023 — Molecular imaging with 18F-flubatine PET/MRI has shown that neuroreceptors in the brains of individuals ...
June 28, 2023 — A newly discovered radionuclide-based agent (CB-2PA-NT) has been shown to have high tumor uptake ...
June 28, 2023 — A novel PET perfusion radiotracer, 18F-flurpiridaz, can diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD) in obese ...
June 27, 2023 — Helen Nadel, MD, FRCPC, director of pediatric nuclear medicine at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at ...
June 26, 2023 — Bayer announced that Ultravist (iopromide)-300, -370, its iodine-based contrast agent, has been approved ...
June 26, 2023 — Nizar A. Mullani, one of the pioneers of the first positron emission tomography (PET) prototype, has ...
June 26, 2023 — Umar Mahmood, MD, PhD, chief of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, director of the Center for ...
June 26, 2023 — PET imaging with 68Ga-FAPI offers a feasible, reliable, and reproducible method for evaluating disease ...
June 26, 2023 — A first-in-human evaluation of the novel theranostic pair 68Ga-DOTA-5G / 177Lu-DOTA-ABM-5G has confirmed ...
June 25, 2023 — A new PET radiotracer that visualizes the enzyme primarily responsible for metabolic cholesterol ...
June 25, 2023 — Julie Dawn Bolin, MS, CNMT, program director of nuclear medicine technology at GateWay Community College ...

 July 12, 2023
July 12, 2023