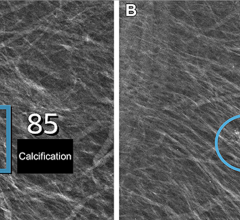
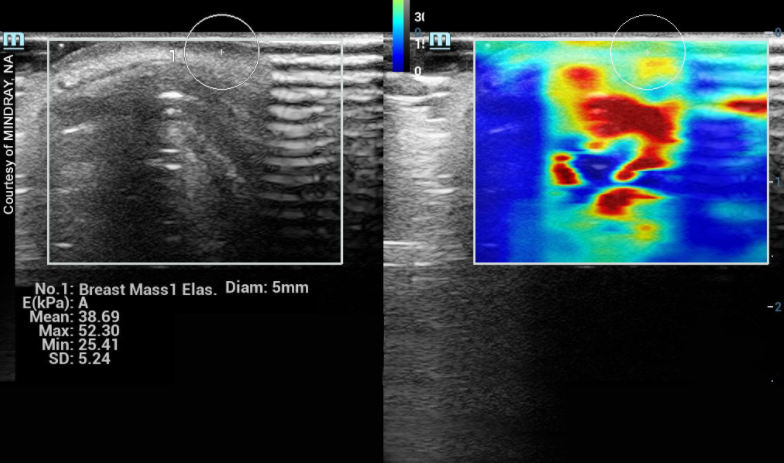
July 17, 2024 — LG Electronics (LG) is accelerating its B2B medical device business, expanding its lineup of diagnostic ...
Breast Imaging
Women's health related to breast imaging, including mammography, breast MRI, ABUS, automated breast ultrasound, breast ultrasound, breast biopsy, PEM and positron emission mammography.
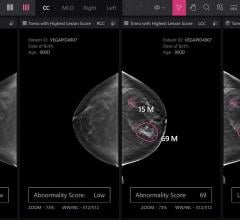
July 9, 2024 — Lunit, a provider of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered solutions for cancer diagnostics and ...
July 5, 2024 — Lantheus Holdings, Inc., a leading radiopharmaceutical-focused company committed to enabling clinicians ...
Despite decades of progress in breast imaging, one challenge continues to test even the most skilled radiologists ...
July 2, 2024 — Delphinus Medical Technologies, a pioneering medical imaging company that developed the SoftVue Breast ...
June 26, 2024 — iCAD, Inc., a global leader in clinically proven AI-powered cancer detection solutions, announced it ...
June 20, 2024 — The technologically advanced VELA Mammography Chair, offered by Enable Me, a VELA Medical company ...
While most women understand the importance of health screenings, an estimated 72 million have missed or postponed a ...
June 18, 2024 — Delphinus Medical Technologies, a pioneering medical imaging company that developed the SoftVue Breast ...
June 12, 2024 — Carestream launched its Image Suite MR 10 Software to help deliver a boost to productivity and ...
June 12, 2024 — Royal Philips recently announced the 1,111th installation of its revolutionary BlueSeal 1.5T magnet ...
The COVID-19 pandemic had a huge impact on the radiology community. Hospitals, doctors’ offices and clinics found ...
June 7, 2024 — Scholars and studies funded by Susan G. Komen(R), the world’s leading breast cancer organization ...
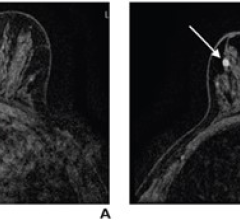
June 6, 2024 — Subsequent rounds of abbreviated breast MRI (AB-MR) screening in patients with dense breasts had lower ...
June 4, 2024 — Using artificial intelligence (AI), breast radiologists in Denmark have improved breast cancer screening ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming more common place in radiology practices, and emerging technologies are ...
As we flip the page to a new month on our calendars, here is a look at the Top 10 pieces of content viewers were reading ...
May 28, 2024 — iCAD, Inc., a global leader in clinically proven AI-powered cancer detection solutions, announced a ...
May 22, 2024 — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued a recall of the Hologic Inc. BioZorb marker due to ...
May 22, 2024 — Lunit, a provider of Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solutions for cancer diagnostics and ...
May 10, 2024 — According to the Summa Cum Laude Award-Winning Online Poster presented during the 124th ARRS Annual ...
May 6, 2024 — ScreenPoint Medical’s Board of Directors has announced the appointment of Peter Kroese as the new Chief ...
May 6, 2024 — Enable Me, a VELA Medical company, cited major new research by Siemens Healthineers entitled, “The future ...
Decades since the advent of breast scanning technology, innovations in noninvasive diagnostic imaging provide new ...


 July 17, 2024
July 17, 2024