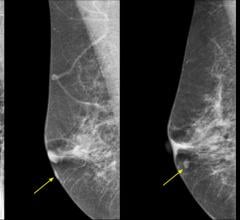
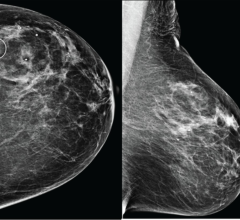
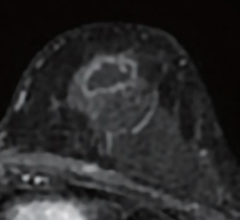
Oct. 28, 2025 — QT Imaging Holdings, Inc., a medical device company focused on radiation-free imaging technology, has ...
Breast Imaging
Women's health related to breast imaging, including mammography, breast MRI, ABUS, automated breast ultrasound, breast ultrasound, breast biopsy, PEM and positron emission mammography.
Despite decades of progress in breast imaging, one challenge continues to test even the most skilled radiologists ...
Oct. 15, 2025 — Leading into Breast Cancer Awareness Month, Fujifilm Healthcare Americas Corp. and Beekley Medical ...
As the largest independent imaging group in Michigan with 10 locations across the state, Regional Medical Imaging (RMI) ...
Oct. 7, 2025 – Clairity Inc., a leader in AI-based breast cancer risk prediction, will make five scientific ...
Oct. 3, 2025 — Gnosis for Her, a mobile breast health initiative redefining comfort and access in women's breast imaging ...
Early detection is key to breast cancer survival. But nearly half of all women in the U.S. have dense breast tissue ...
Christina Jacobs, M.D., Director of Breast Imaging (Bronson Health System) is always looking for ways to work more ...
Sept. 26, 2025 — Data from two groundbreaking studies evaluating the performance of Hologic’s artificial intelligence ...
Sept. 20, 2025 — A promising new PET tracer can visualize a protein that is commonly overexpressed in triple-negative ...
Sept. 3, 2025 — According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a commercial artificial intelligence (AI) ...
ProFound AI is an FDA-cleared artificial intelligence (AI) system for reading 3-D breast tomosynthesis images. At RSNA19 ...
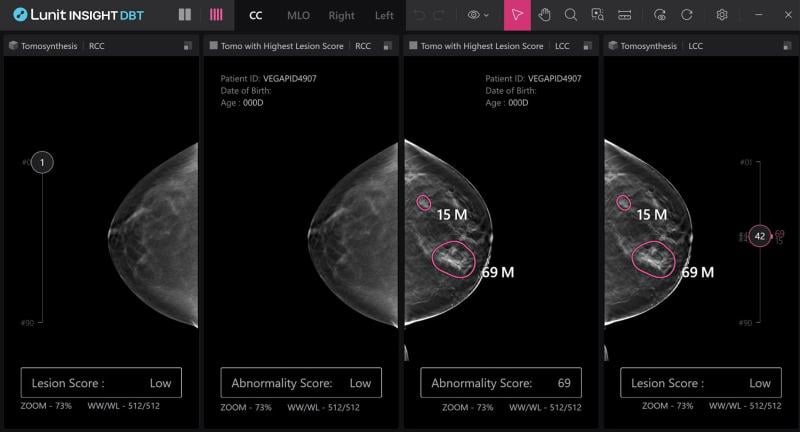
August 18, 2025 – Akumin, a national leader in outpatient radiology and oncology services, has selected Lunit INSIGHT ...
Aug. 19, 2025 — According to the latest study from BCC Research, the "Global Mammography Equipment Markets" is projected ...
Aug. 19, 2025 — Calidar, Inc., a start-up in precision diagnostic imaging formed out of Duke University, recently ...
At RSNA19, David Widmann, president and CEO of Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, discussed innovation, stressing the ...
Aug. 5, 2025 — New Lantern has announced the launch of two specialized viewer modes: the Mammography Viewer Mode and PET ...
Aug. 1, 2025 — The American Roentgen Ray Society’s American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) has published a clinically ...
July 29, 2025 — A new technology that harnesses AI to analyze mammograms and improve the accuracy of predicting a woman ...
QT Imaging Holdings, Inc. has announced the launch of its latest QTviewer, version 2.8. QTviewer stores and displays the ...
July 17, 2025 — RadNet, Inc., a provider of high-quality, cost-effective diagnostic imaging services and digital health ...
July 8, 2025 — QT Imaging Holdings, has appointed Elaine Iuanow, MD, as chief medical officer (CMO) and Kim Du as senior ...
July 7, 2025 — SimonMed Imaging, one of the largest outpatient medical imaging providers in the United States, has ...
June 25, 2025 — QT Imaging Holdings, Inc., a medical device company engaged in research, development, and ...


 October 28, 2025
October 28, 2025