
Pre-processing results. Image courtesy of Applied Sciences.
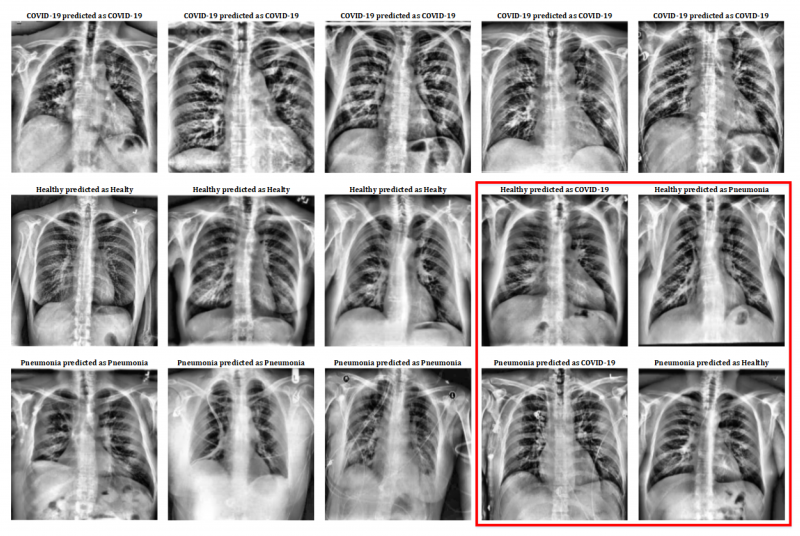
July 22, 2020 — Researchers from the Department of Computer Architecture and Technology at the University of Seville's School of Computer Engineering (ETSII) are working on a system that uses X-ray images of patients' lungs to help diagnose COVID-19. This system uses deep learning to train a neural network model that can distinguish between healthy patients, pneumonia patients and COVID-19 patients. This has been achieved using a freely accessible online database that medical professionals from around the world have been feeding with lung X-rays since the onset of the pandemic.
"The spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus has turned COVID-19 into a global epidemic. The most commonly-used tests to diagnose the disease are invasive, time-consuming and resource-limited. Images obtained from magnetic resonances and/or X-rays are increasingly being used to facilitate diagnostic assistance tasks, having been successfully tested to identify lung problems. However, these diagnostic methods require a specialist, which limits mass uptake among the population," said University of Seville professor Manuel Jesús Domínguez. The researcher adds that processing tools can help reduce health professionals' workload by filtering out negative cases. In particular, advanced artificial intelligence techniques such as deep learning have proven highly effective in identifying patterns such as those found in diseased tissue.
Similarly, this work analyses the effectiveness of a deep learning model based on a VGG-16 neural network for the identification of pneumonia and COVID-19 using X-rays of the torso. The results, published in the journal Applied Sciences, reveal that this method is around 100% effective in the identification of COVID-19, proving that it can be used as an aid to diagnose this disease.
For more information: www.
Related Coronavirus Content:
VIDEO: Imaging COVID-19 With Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Cardiac Imaging Best Practices During the COVID-19 Pandemic
RSNA Publishes COVID-19 Best Practices for Radiology Departments
ASE Guidelines for the Protection of Echocardiography Providers During the COVID-19 Outbreak
New CT Scoring Criteria for Timely Diagnosis, Treatment of Coronavirus Disease
FDA Issues New Policy for Imaging Systems During COVID-19
VIDEO: COVID-19 Precautions for Cardiac Imaging — Interview with Stephen Bloom, M.D.
A Review of Studies Cautions Against Chest CT for Coronavirus Diagnosis
New Research Finds Chest X-ray Not Reliable Diagnostic Tool for COVID-19
VIDEO: Radiology Industry Responding to COVID-19
University of Washington Issues Radiology Policies for COVID-19
VIDEO: Best Practices for Nuclear Cardiology During the COVID-19 Pandemic — Interview with Hicham Skali, M.D.
New Research Highlights Blood Clot Dangers of COVID-19
Survey Reveals Most Medical Practices are Now Using Telehealth Due to COVID-19
CMS Offers Recommendations on Reopening Healthcare in Areas of Low COVID-19 Cases
CT Provides Best Diagnosis for Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Radiology Lessons for Coronavirus From the SARS and MERS Epidemics
Radiologists Describe Coronavirus CT Imaging Features
CT Imaging of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Pneumonia
ACC COVID-19 recommendations for the cardiovascular care team
VIDEO: What Cardiologists Need to Know about COVID-19 — Interview with Thomas Maddox, M.D.


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









