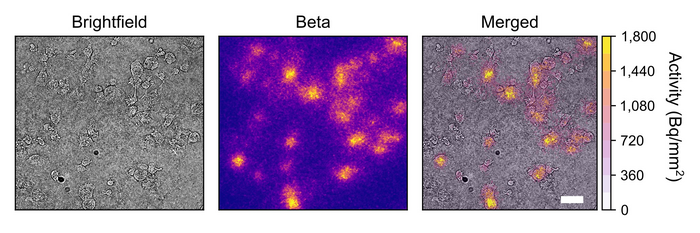
High-resolution beta imaging of 18F-FDG in breast cancer cells. MDA-MB-231 cells were imaged using brightfield and beta modes. Images are cropped to 600 mm × 600 mm from the full 3.7 mm × 2.8 mm field of view. Total imaging time for beta imaging was 65 minutes. Scale bar is 50 mm. Image created by Justin Klein, Stanford University, Stanford, California.
March 22, 2023 — A novel imaging modality that can visualize the distribution of medical radiopharmaceuticals with very fine resolution has been developed and successfully tested, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Known as the lensless radiomicroscope, the palm-sized instrument offers the same level of imaging performance as its closest imaging equivalent but comes with significantly larger field of view and costs less than $100.
“While many nuclear medicine imaging modalities can quantitively measure how radiopharmaceuticals interact with living tissues, few have the resolution necessary to zoom down to level of single cells,” said Guillem Pratx, PhD, associate professor of radiation oncology at Stanford University in Stanford, California. “This potentially hinders the development of effective radiopharmaceuticals for disease detection, staging, and treatment.”
To address this issue, researchers constructed a compact instrument that images radiopharmaceuticals by direct detection of ionizing charged particles via a consumer-grade complementary metal-oxide semiconductor detector. It is made from off-the-shelf parts that cost less than $100, which is approximately 500 times less than the radioluminescence microscope, the closest imaging device to the lensless microscope.
Upon proof-of-concept testing, the lensless radiomicroscope produced high-resolution images of more than 5,000 cells within its 1 cm2 field of view, a hundredfold increase over current state-of-the-art technology. Static and dynamic images were successfully created for both beta- and alpha-emitting radionuclides with the lensless radiomicroscope.
“With these improvements, we expect that the new lensless radiomicroscope will be available for more labs to incorporate into their studies,” noted Pratx. “Researchers will be able to analyze the uptake of radiotracers by heterogeneous populations of cells, such as those extracted from tumors or the brain. This in turn, will provide an opportunity for researchers to incorporate cellular level data into the development pipeline of new radiopharmaceuticals.”
Currently the lensless radiomicroscope design is available to other researchers as open source. The instrument can be built using consumer grade components and 3-D printing.
This study was made available online in September 2022.
For more information: www.snmmi.org


 March 12, 2026
March 12, 2026 









