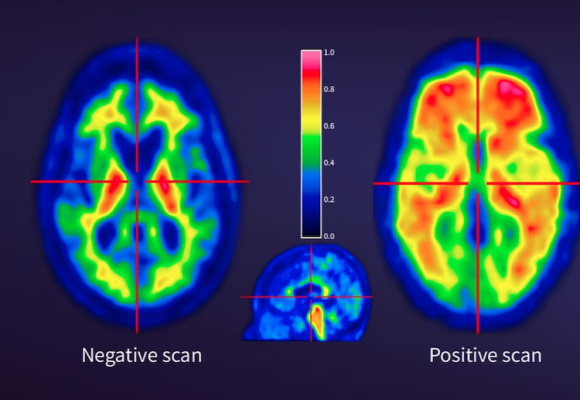
Jun. 24, 2025 — GE HealthCare has announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an updated label for its positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent Vizamyl (flutemetamol F 18 injection) for beta-amyloid detection. The revised label, effective immediately, expands the indications for use, enables quantitative analysis of Vizamyl scans, and removes significant previous limitations such as monitoring patient response to anti-amyloid therapy.
Up to now, amyloid diagnostics such as Vizamyl have been used to provide a visual assessment of amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain. With quantification now added to the label, clinicians can reach a more objective assessment, using software that enables a calculation of amyloid load, with published research demonstrating that quantification improves diagnostic confidence and consistency among readers1,2,3. In addition, with the removal of a limitation of use for monitoring therapy effectiveness, Vizamyl can also now be used to assess whether the level of amyloid plaques has been reduced sufficiently for the therapy to potentially be stopped.
“The inclusion of quantification and removal of the therapy monitoring limitation from the Vizamyl label is good news for healthcare providers and their patients, further enabling timely and appropriate care decisions,” said Jit Saini, MD, Chief Medical Officer of the Pharmaceutical Diagnostics (PDx) division of GE HealthCare. “These changes pave the way for clinicians to expand their usage of Vizamyl, with meaningful implications for patients and their families— helping provide clearer answers, earlier diagnoses, and enabling more personalized treatment strategies.”
“The use of quantification in amyloid PET imaging has steadily moved from research to clinical practice, where it can aid in more confident and accurate diagnosis,” said Phillip Kuo, MD, PhD, FACR, Professor of Radiology, Section Chief of Nuclear Medicine and Director Theranostics at City of Hope National Medical Center. “Now quantification can also play a critical role in initiating and monitoring amyloid-targeted therapy for Alzheimer's disease and determining when it can be discontinued.”
The label update also adds an explicit indication for selection of patients eligible for therapy and removes several previous limitations of use, including for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, based on revised criteria from the Alzheimer’s Association, indicating that an abnormal amyloid PET scan is sufficient to establish a diagnosis. Furthermore, the label now removes a previous limitation on predicting the cognitive decline or progression to dementia, based on evidence linking amyloid-positive scans to a higher risk of progression from the early mild cognitive impairment phase of Alzheimer’s dementia4.
Vizamyl was first approved in 2013 to estimate beta amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment. GE HealthCare offers solutions for quantitative analysis of amyloid PET scans including through its MIM Neuro Software platform which has been recently FDA cleared for centiloid scaling.
Learn more about Vizamyl at GE HealthCare’s PDx booth 1029 at the SNMMI 2025 Annual Meeting June 21 – 24 in New Orleans, LA or online at www.gehealthcare.com/products/molecular-imaging-agents/vizamyl.
[1] Collij LE, Bischof GN, Altomare D et al. Quantification Supports Amyloid PET Visual Assessment of Challenging Cases: Results from the AMYPAD Diagnostic and Patient Management Study. J Nucl Med. 2025 Jan 3;66(1):110-116.
[2] Collij LE, Salvadó G, Shekari M et al. Visual assessment of [(18)F]flutemetamol PET images can detect early amyloid pathology and grade its extent. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Jul;48(7):2169-2182.
[3] Bucci M, Savitcheva I, Farrar G et al, A multisite analysis of the concordance between visual image interpretation and quantitative analysis of [(18)F]flutemetamol amyloid PET images. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Jul;48(7):2183-2199.
[4] www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia/related_conditions/mild-cognitive-impairment, accessed on June 19, 2025

 March 04, 2026
March 04, 2026