March 23, 2021 — iCad announced that ProFound AI Version 3.0 for Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Compared to previous versions of the software, the ProFound AI 3.0 algorithm offers up to a 10% improvement in specificity performance and up to 1% improvement in sensitivity.[i] ProFound AI Version 3.0 also offers up to 40% faster processing on the new PowerLook platform.
“The FDA Clearance of ProFound AI Version 3.0 is yet another milestone that positions iCAD and our technology as vanguards in the cancer detection realm. Our third generation AI solution for DBT may afford physicians the ability to interpret an increasing amount of data in DBT cases and analyze each image to detect malignant lesions more efficiently and with even greater precision,” said Michael Klein, Chairman and CEO of iCAD. “Improvements in specificity, which correlates with reductions in false positives, typically come at the expense of sensitivity and cancer detection scores. To increase sensitivity while simultaneously improving specificity is a huge performance achievement.”
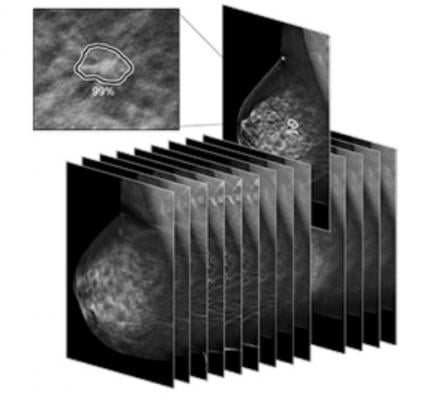
ProFound AI for DBT is a high-performance, deep-learning, workflow solution trained to detect malignant soft tissue densities and calcifications. It became the first 3D tomosynthesis software using artificial intelligence (AI) to be FDA cleared in December 2018.
Built with the latest in deep-learning technology, ProFound AI for DBT rapidly analyzes each tomosynthesis image, detecting malignant soft tissue densities. Certainty of Finding and Case Scores are relative scores computed by the ProFound AI algorithm and represent its confidence that a detection or case is malignant. The Certainty of Finding scores help radiologists by aiding in clinical decision making. Case Scores, which are assigned to each case by the algorithm, help clinicians to gain a sense of case complexity, which may be useful for prioritizing the reading work list.
“Late last year we made the decision to go enterprise-wide with ProFound AI,” said Alexander Sardiña, M.D., Chief Medical Officer for Solis Mammography. “From a patient perspective, improved specificity and sensitivity means that we can minimize the anxiety caused by false positives and recalls, without compromising cancer detection rates. This is a significant achievement. We’re excited to put this technology to work – on behalf of our patients – across our national network of facilities.”
In a reader study published in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, ProFound AI for DBT Version 2.0 was shown to offer clinically proven time-savings benefits to radiologists, reducing reading time by 52.7 percent, improving radiologist sensitivity by 8 percent, and reducing false positives and unnecessary patient recall rates by 7.2 percent.[ii]
iCAD’s Breast Health Solutions suite also includes ProFound AI for 2D Mammography, ProFound AI Risk, the world’s first and only clinical decision support tool that provides an accurate two-year, breast cancer risk estimation that is truly personalized for each woman, based only on a screening mammogram,[iii] and software to evaluate breast density.
For more information: www.icadmed.com
[i] *iCAD data on file. Standalone performance varies by vendor. FDA Cleared.
[ii] Conant, E et al. (2019). Improving Accuracy and Efficiency with Concurrent Use of Artificial Intelligence for Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 1 (4). Accessed via https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/ryai.2019180096
[iii] Eriksson M, Czene K, Strand F, et al. Identification of Women at High Risk of Breast Cancer Who Need Supplemental Screening. [published online ahead of print September 8, 2020]. Radiology. Accessed via https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020201620


 March 11, 2026
March 11, 2026 









