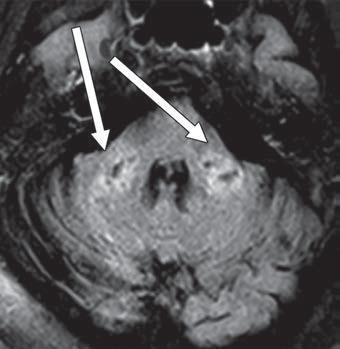
Axial FLAIR MR image shows T2 prolongation in bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles (arrows). Findings were associated with restricted diffusion and areas of T1 hypointense signal without enhancement or abnormal susceptibility. Image courtesy of American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
February 22, 2021 — According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), COVID-19-related disseminated leukoencephalopathy (CRDL) represents an important--albeit uncommon--differential consideration in patients with neurologic manifestations of coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
"Increasingly," wrote Colbey W. Freeman and colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania, "effects of COVID-19 on the brain are being reported, including acute necrotizing encephalopathy, infarcts, microhemorrhage, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and leukoencephalopathy."
Among the 2,820 patients with COVID-19 admitted to the authors' institution between March 1 and June 18, 2020, 59 (2.1%) underwent brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI0https://www.itnonline.com/chart/mri-wide-bore-systems. Three (5.1%) had known white matter lesions from multiple sclerosis, 23 (39.0%) had white matter lesions of small vessel ischemic disease, six (10.2%) had acute infarcts, four (6.8%) had subacute infarcts, four (6.8%) had chronic infarcts, one (1.7%) had abnormal basal ganglia signal from hypoxemia, two (3.4%) had microhemorrhage in association with chronic infarcts, and two (3.4%) had microhemorrhage associated with acute or subacute infarcts.
Six patients (10.2%; four women, two men; age range, 41-86 years) had neuroimaging findings suggestive of CRDL—"characterized by extensive confluent or multifocal white matter lesions (with characteristics and locations atypical for other causes), microhemorrhages, diffusion restriction, and enhancement," Freeman et al. explained. Hypertension (4/6, 66.7%) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (3/6, 50.0%) were common comorbidities.
Reiterating that no established criteria exist for defining CRDL, "our patients had white matter lesions atypical for other causes," as well as "involvement of the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles and corpus callosum," the authors of this AJR article concluded.
For more information: www.arrs.org
Related COVID-19 Content:
Early Details of Brain Damage in COVID-19 Patients
How COVID-19 Affects the Brain in Neuroimaging
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
VIDEO: COVID Vaccine May Cause Enlarged Lymph Nodes on Mammograms — Interview with Constance "Connie" Lehman, M.D.
VIDEO: How to Image COVID-19 and Radiological Presentations of the Virus — Interview with Margarita Revzin, M.D.


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









