July 10, 2025 — Fujifilm Healthcare Americas Corp. has launched several advanced automated functions for its FDR Visionary Suite digital radiography room. Optimized to support high-volume imaging in hospital radiology departments and imaging centers, the automation features are designed to enhance
July 15, 2025 — Radiology Partners (RP), a provider of technology-enabled radiology services, has announced the launch ...
The American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), in Albuquerque, N.M., was recently recognized by the ...
July 14, 2025 — Patients with liver diseases will have expanded access to advanced ultrasound imaging and transplant ...
eHealth Saskatchewan plays a vital role in providing IT services to patients, health care providers, and partners such ...
July 10, 2025 — Bracco Imaging was recently awarded a Platinum Medal by EcoVadis, one of the world's most trusted ...
July 10, 2025 — Fujifilm Healthcare Americas Corp. has launched several advanced automated functions for its FDR ...
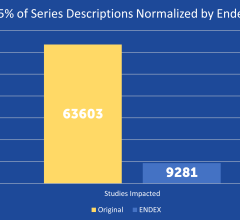
SPONSORED CONTENT — EnsightTM 2.0 is the newest version of Enlitic’s data standardization software framework. Ensight is ...
June 9, 2025 — bioAffinity Technologies, Inc., a biotechnology company addressing the need for noninvasive, accurate ...
While most women understand the importance of health screenings, an estimated 72 million have missed or postponed a ...
July 9, 2025 — Artera, the developer of multimodal artificial intelligence (MMAI)-based prognostic and predictive cancer ...
July 9, 2025 — The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) selected 43 members to receive the ASTRO Fellow ...
July 8, 2025 — QT Imaging Holdings, has appointed Elaine Iuanow, MD, as chief medical officer (CMO) and Kim Du as senior ...
Fujifilm’s APERTO Lucent is a 0.4T mid-field, open MRI system addressing today’s capability and image quality needs ...
July 2, 2025 — Lunit, a provider of AI for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics, has announced a collaboration with ...
July 7, 2025 — SimonMed Imaging, one of the largest outpatient medical imaging providers in the United States, has ...
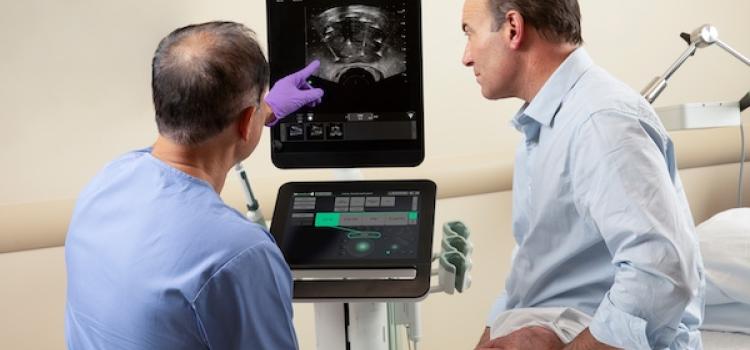
July 8, 2025 — Mendaera, Inc., a healthcare technology company focused on developing robotics that can be deployed ...
SPONSORED CONTENT — Fujifilm’s latest CT technology brings exceptional image quality to a compact and user- and patient ...
July 01, 2025 — NANO-X Imaging Ltd. recently announced a clinical and educational collaboration with Keiser University ...
July 2, 2025 — Philips has received FDA 510(k) clearance for SmartSpeed Precise[1] MR’s latest deep learning ...
A new study published in JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics tackles a critical challenge in cancer diagnostics: ensuring ...
July 1, 2025 — UPDATE: The final paper is now available at: JMIR AI - ChatGPT-4–Driven Liver Ultrasound Radiomics ...
June 26, 2025 — FUJIFILM VisualSonics Inc., a provider of ultra-high frequency ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging ...
June 18, 2025 — Probo Medical, a provider of medical imaging equipment, service, and support, has announced a strategic ...
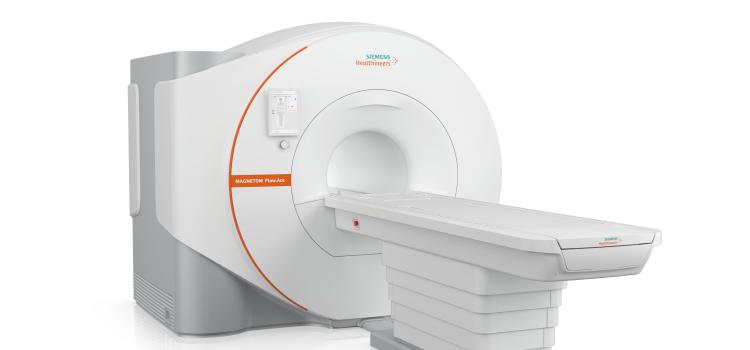
June 26, 2025 — Siemens Healthineers has received Food and Drug Administration clearance for the Magnetom Flow.Ace, its ...
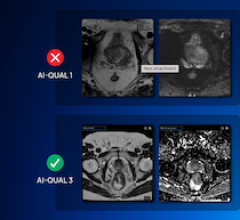
June 26, 2025 – Quibim, a global provider of quantitative medical imaging solutions, has launched AI-QUAL, a new feature ...



![CEDM[1] copy](/sites/default/files/styles/slider/public/CEDM%5B1%5D%20copy.png?itok=XK5AvT8Q)

 July 15, 2025
July 15, 2025