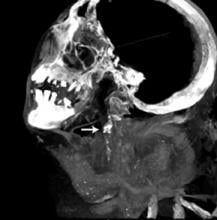
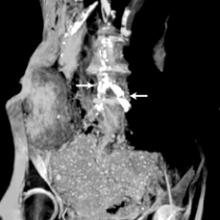
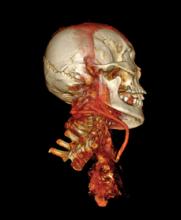
Incidents of cancer are on the rise globally. According to a press release from the World Health Organization’s (WHO) International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), “In 2012, the worldwide burden of cancer rose to an estimated 14 million new cases per year, a figure expected to rise to 22 million annually in the next decade.” As the numbers increase around the world, research continues to unveil unconventional options for cancer treatment. Over the past five years, proton therapy has emerged as one popular choice. Hailed by some as the Rolls Royce of radiation oncology, the technology’s precision and accuracy, along with its ability to prevent damage to critical structures and healthy tissues, has made it a technology that many vendors and healthcare facilities are actively investing in.
If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
- Read more about Pushing Proton Therapy
- Log in or register to post comments