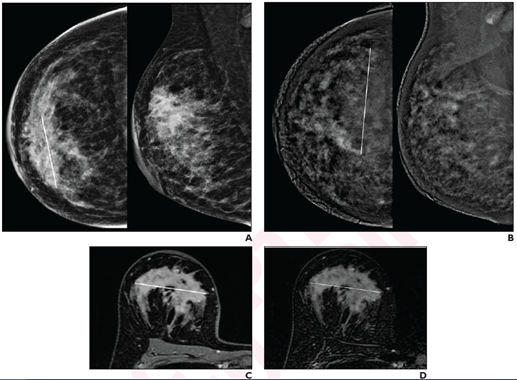
41-year-old woman with invasive ductal carcinoma (G2, luminal B) of right breast. A, CC (left) and MLO (right) low-energy images from pre-NAT CEM performed on 25th day of luteal phase show a 60-mm architectural distortion (line on CC) in the central portion of the right breast. B, CC (left) and MLO (right) recombined images from pre-NAT CEM show marked background parenchymal enhancement, hindering lesion evaluation; 90-mm non-mass regional enhancement (line) was described. C, Axial fat-saturated T1-weighted unenhanced MR image shows a 70-mm hypointense irregular mass (line) with not circumscribed margins in the central portion of right breast. D, Axial fat-saturated T1-weighted post-contrast MR images shows corresponding fast initial enhancement (line) with delayed plateau.
June 22, 2022 — According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) may be a useful alternative test for neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) response assessment in patients with breast cancer who are unable to undergo MRI.
“After NAT for breast cancer, CEM and MRI yielded comparable assessments of lesion size (both slightly overestimated vs pathology) and RECIST categories, and no significant difference in specificity for pathologic complete response,” wrote corresponding author Rubina Manuela Trimboli of IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital in Milan, Italy. Noting that MRI had higher sensitivity for pathologic complete response, “delayed CEM acquisition may help detect residual ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).”
Trimboli and team’s prospective study included 51 patients (mean age, 46 years) with biopsy-proven breast cancer from May 2015 to April 2018, who were candidates for NAT. Patients underwent both CEM and MRI before, during, and after NAT: pre-NAT, mid-NAT, and post-NAT, respectively. Post-NAT CEM included a 6-minute delayed acquisition. One breast radiologist with experience in CEM reviewed CEM examinations; one breast radiologist with experience in MRI reviewed MRI examinations.
Compared with pathology, post-NAT CEM, MRI, and delayed CEM systematically overestimated residual tumor size by 0.8 mm, 1.9 mm, and 1.2 mm, respectively. For detecting pathologic complete response by post-NAT imaging, sensitivity and specificity were 81% and 83% for CEM, 100% and 86% for MRI, and 81% and 89% for delayed CEM.
“While MRI remains the preferred test for NAT monitoring,” the authors of this AJR article concluded, “the findings support CEM as a useful alternative when MRI is contraindicated or not tolerated.”
For more information: www.arrs.org
Related Digital Breast Imaging Content:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Spot Compression Clarifies Ambiguous Findings
AI DBT Impact on Mammography Post-breast Therapy
ImageCare Centers Unveils PINK Better Mammo Service Featuring Profound AI
Radiologist Fatigue, Experience Affect Breast Imaging Call Backs
Fewer Breast Cancer Cases Between Screening Rounds with 3-D Mammography
Related Breast MRI content:
Contrast-Enhanced In-Phase Dixon Sequence: Impact on Biopsy Clip Detection on Breast MRI
Breast MRI Illuminates Risk of Second Breast Cancer
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography vs. MRI: Neoadjuvant Therapy Response in Breast Cancer
Breast MRI Shows IUDs Have Systemic Effects
VIDEO: Use of Breast MRI Screening in Women With Dense Breasts — Interview with Christiane Kuhl, M.D.
Abbreviated MRI Outperforms 3-D Mammograms at Finding Cancer in Dense Breasts
VIDEO: Explaining Dense Breasts — Interview with Christiane Kuhl, M.D.
VIDEO: Use of Breast MRI Improved Cancer Detection in Dense Breasts in Dutch Study — Interview with Gillian Newstead, M.D.
Technologies to Watch in Breast Imaging
Screening MRI Detects BI-RADS 3 Breast Cancer in High-risk Patients
Rapid Breast MRI Screening Improves Cancer Detection in Dense Breasts


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









