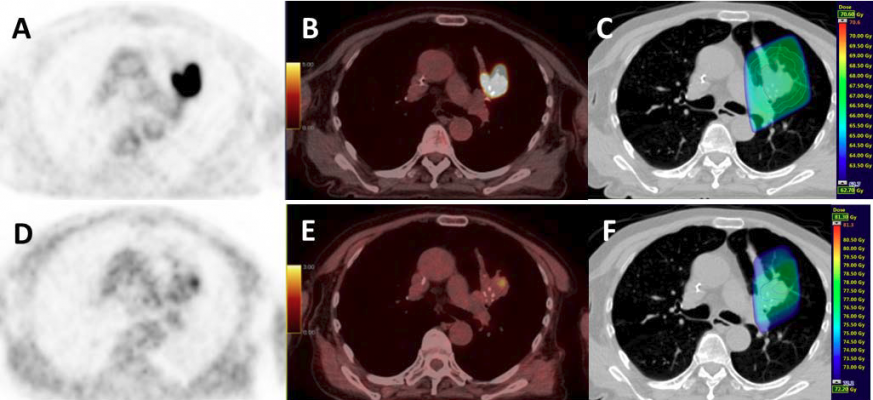
Example of a patient with an upper left lung NSCLC: A: FDG; B: FDG PET/CT; C: Planning radiotherapy based on FDG (66Gy) with BTVm (GTV), CTV and PTV; D: PET FMISO E: FMISO PET/CT; F: boost based on the FMISO PET (76Gy) with BTVh (biological hypoxic target volume) and PTV boost. Credit: QuantIF – LITIS EA 4108 – FR CNRS 3638, Henri Becquerel Cancer Center, Rouen, France
July 14, 2017 — Fluorine-18 (18F)-fluoromisonidazole (FMISO) is a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer that is widely used to diagnose hypoxia and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with FMISO uptake are known to face a poor prognosis. A multicenter French Phase II study featured in the July issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) investigated whether a selective radiotherapy (RT) dose increase to tumor areas with significant FMISO uptake in NSCLC patients could improve outcomes.
The study, conducted by 15 academic PET facilities across France, evaluated 54 patients with localized, advanced non-small cell cancers, who were undergoing chemoradiotherapy. For each patient, two FDG-PET/CT (computed tomography) and two FMISO-PET/CT scans were performed using the same machine and under the identical operational conditions. Quality control was centrally supervised to secure homogeneity in the image quality in all participating centers. In 24 of the patients, the radiotherapy dose could be increased up to 86 Gy on hypoxic areas identified on FMISO PET/CT. Unfortunately, this dose increase did not improve patient outcomes.
On the bright side, Pierre Vera, M.D., Ph.D., of the Henri Becquerel Cancer Center and Rouen University Hospital in Rouen, France, noted, "We demonstrate that this approach of radiotherapy boost based on hypoxia PET is feasible in a multicenter setting. Regarding the clinical aspect, a recent randomized trial (Bradley Lancet Oncol 2015) failed to demonstrate the benefit of escalated radiotherapy dose in large target volumes. Our data show that smaller volumes, identified on their functional characteristics using hypoxia PET/CT, can be adequately targeted. In addition, no significant toxicity has been observed in patients receiving radiotherapy boost."
In an invited perspective, also published in the July JNM, Rodney J. Hicks, M.D., FRACP, FAHMS, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and the University of Melbourne in Melbourne, Australia, points out that negative results are instructive. He stated, "Clearly, hypoxia remains an evil foe in our battle to achieve better outcomes in non-small cell cancer. But by demonstrating its importance, Vera and colleagues pose us the challenge to design new combination therapies. ...[For example,] there may be synergy between radiation and check-point immunotherapy."
For more information: www.jnm.snmjournals.org


 February 27, 2026
February 27, 2026