Photo credit: Ascelia Pharma
December 3, 2022 — Results from its Orviglance Food Effect study were presented by Ascelia Pharma, a biopharmaceutical company focused on improving the lives of people with rare cancers, during RSNA 2022, the Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, which took place Nov. 27-Dec. 1, 2022, in Chicago, IL.
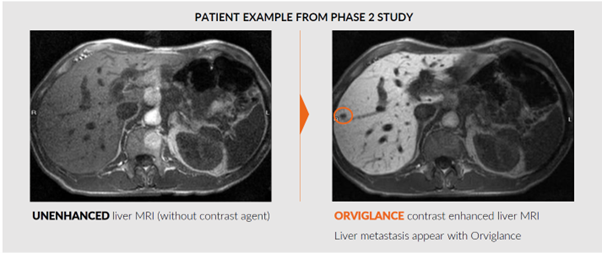
The study evaluated the effect of food intake on the absorption and signal intensity of Orviglance, a manganese-based MRI contrast agent, and successfully concluded that image enhancement is not impacted by a light meal.
The Food Effect Study evaluates the effect of food intake on absorption and signal intensity of Orviglance, Ascelia Pharma’s investigational magnetic resonance-imaging (MRI) agent used in the visualization and detection of cancer in the liver in patients with reduced kidney function. The results show that intake of a light meal within 30 min prior to Orviglance administration provides similar image MRI enhancement of the liver compared to a fasting condition. In line with previous studies, the data also confirms strong image enhancement of the liver after Orviglance administration compared to an MRI image without a contrast agent. In clinical practice, the results demonstrate the possibility of being administered Orviglance both after fasting or after consumption of a light meal.
“The possibility for omitting a fasting condition improves the convenience for patients and eases the administration of Orviglance in clinical practice,” according to Magnus Corfitzen, CEO at Ascelia Pharma. In a statement issued by the company, Corfitzen said he was pleased Ascelia Pharma was presenting the study as an oral presentation during RSNA 2022.
“The study provides robust evidence of the diagnostic value that Orviglance can offer once it is available to patients and physicians. Orviglance is being developed to address the unmet medical need of patients with poor kidney function who require liver imaging, and it is very encouraging that the study results support previous findings on the ability of Orviglance to provide strong image enhancement to liver MRI scans,” he added.
In this crossover study, Orviglance was administered to 24 healthy volunteers in fasting condition and in one of two conditions with food intake (either a light or full meal). The image enhancement effect was measured by the change in the MR signal intensity before and after (1, 4, 8 and 24 hours) administration of Orviglance. The results showed that a light meal prior to Orviglance administration provided similar image enhancement when compared to a fasting condition, whereas the image enhancement was less pronounced for the group receiving a full meal. Ascelia Pharma has filed a patent application based on the results of the study.
The reporting of these final results for the Food Effect Study completes two of the three studies in Ascelia Pharma’s ongoing Phase 3 clinical program for registration of Orviglance. A Hepatic Impairment Study successfully concluded that Orviglance is well tolerated in patients with liver (hepatic) impairment, with only mild to moderate transient, gastrointestinal adverse events reported, such as nausea. No new safety concerns were identified. The data confirmed there was no renal excretion of Orviglance, and that excretion is primarily occurring via the liver also in this subgroup of patients.
The plan for the ongoing Phase 3 study, SPARKLE, required for a subsequent regulatory submission, is to complete patient enrolment by the end of this year. Data from all three studies will be included in the marketing authorization application to health authorities, including FDA and EMA.
Orviglance is a novel manganese-based oral contrast agent for MRI developed to improve the detection and visualization of focal liver lesions (including liver metastases and primary tumors) in patients with reduced kidney function. These patients are at risk of serious, and potentially fatal, side effects from the currently available class of gadolinium-based contrast agents, which all carry black box warnings issued by regulatory authorities, such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) because of this risk. Orviglance, which has been granted an Orphan Drug Designation by the FDA, is currently in Phase 3 development.
SPARKLE is a global multicenter study of Orviglance in up to 200 patients with severe renal impairment and known or suspected focal liver lesions. Primary efficacy, in terms of lesion visualization compared to unenhanced MRI (MRI without a contrast agent), will be evaluated by three independent blinded readers.
For more information, visit www.ascelia.com.

 March 04, 2026
March 04, 2026 









