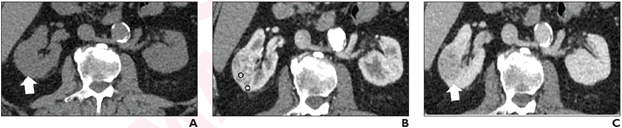
72-year-old man with right interpolar 3.2-cm renal mass. Axial CT images in the (A) unenhanced, (B) corticomedullary, and (C) nephrographic phases at the same level depict the mass (arrow, A and C), which shows avid heterogeneous enhancement. Circular ROIs were placed in the most enhancing component of the mass and in ipsilateral renal cortex (circles, B), to determine the mass-to-cortex corticomedullary attenuation ratio. Heterogeneity scores were assigned subjectively using a 5-point Likert type-scale. These two features were used to inform development of the CT score. In this patient, the mass showed avid enhancement (mass-to-cortex corticomedullary enhancement ratio >0.75) and was considered completely heterogeneous (heterogeneous score, 5) by both radiologists, resulting in CT score 5. Nephrectomy revealed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
June 30, 2022 — According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a 5-tiered CT scoring algorithm may represent a clinically useful tool for diagnosis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in small (≤4 cm) solid renal masses.
“A 5-tiered renal CT algorithm, including mass-to-cortex corticomedullary attenuation ratio and heterogeneity score, had substantial inter-observer agreement, moderate AUC and PPV, and high NPV for diagnosing clear-cell RCC,” concluded Nicola Schieda from the department of medical imaging at Canada’s Ottawa Hospital.
Schieda and colleagues’ study included 148 patients (mean age, 58 years; 73 men, 75 women) with 148 small (≤4 cm) solid (>25% enhancing tissue) renal masses that underwent renal-mass CT (unenhanced, corticomedullary, and nephrographic phases) before resection between January 2016 and December 2019. Two radiologists independently evaluated CT examinations and recorded calcification, mass attenuation in all phases, mass-to-cortex corticomedullary attenuation ratio, and heterogeneity score (5-point Likert scale, assessed in corticomedullary phase).
Ultimately, Schieda et al’s 5-tiered CT scoring algorithm—including mass-to-cortex corticomedullary attenuation ratio and heterogeneity score—had substantial interobserver agreement (weighted kappa=0.71) and achieved AUC for diagnosing clear-cell RCC of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.68-0.82) for reader 1 and 0.72 (95% CI, 0.66-0.82) for reader 2.
“If validated,” the authors of this AJR article acknowledged, “the CT algorithm may represent a useful clinical tool for diagnosing clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.”
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026