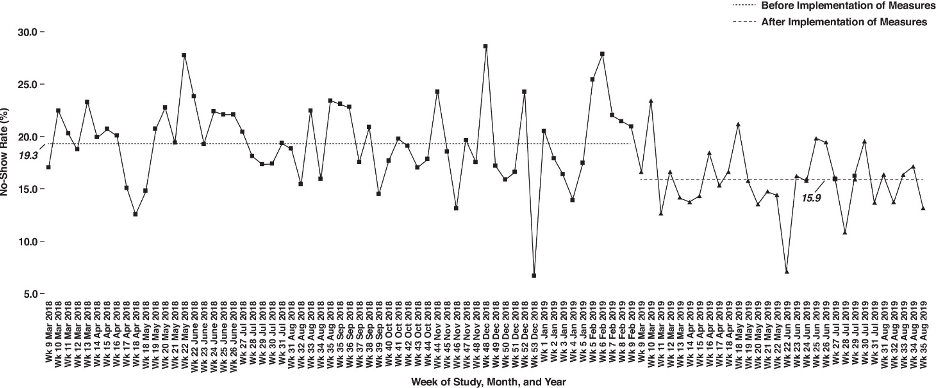
Weekly outpatient MRI appointment no-show rates for 1 year before (19.3%) and 6 months after (15.9%) implementation of intervention measures in March 2019, as guided by XGBoost prediction model. Squares denote data points. Courtesy of the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
September 10, 2020 — According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), artificial intelligence (AI) predictive analytics performed moderately well in solving complex multifactorial operational problems — outpatient MRI appointment no-shows, especially — using a modest amount of data and basic feature engineering.
“Such data may be readily retrievable from frontline information technology systems commonly used in most hospital radiology departments, and they can be readily incorporated into routine workflow practice to improve the efficiency and quality of health care delivery,” wrote lead author Le Roy Chong of Singapore’s Changi General Hospital.
To train and validate their model, Chong and colleagues extracted records of 32,957 outpatient MRI appointments scheduled between January 2016 and December 2018 from their institution’s radiology information system, while acquiring a further holdout test set of 1,080 records from January 2019. Overall, the no-show rate was 17.4%.
After evaluating various machine learning predictive models developed with widely used open-source software tools, Chong and team deployed a decision tree-based ensemble algorithm that uses a gradient boosting framework: XGBoost, version 0.80 [Tianqi Chen].
As Chong et al. explained, “the simple intervention measure of using telephone call reminders for patients with the top 25% highest risk of an appointment no-show as predicted by the model was implemented over 6 months.”
Six months after deployment, the no-show rate of the predictive model was 15.9%, compared with 19.3% in the preceding 12-month preintervention period — corresponding to a 17.2% improvement from the baseline no-show rate (p < 0.0001). The no-show rates of contactable and noncontactable patients in the group at high risk of appointment no-shows as predicted by the model were 17.5% and 40.3%, respectively (p < 0.0001).
Weekly outpatient MRI appointment no-show rates for 1 year before (19.3%) and 6 months after (15.9%) implementation of intervention measures in March 2019, as guided by XGBoost prediction model. Squares denote data points.
“We believe that the main strength of the present study lies in its empirical approach, given the lack of published literature quantifying the impact of actual workflow implementation, with previous studies postulating the potential benefits of applying machine learning techniques to this problem,” the authors of this AJR article concluded. “The aim of our study was not to produce a highly complex model but, rather, to produce one that could be developed relatively quickly, would require minimal data processing, and would be readily deployable in workflow practice for quality improvement.”
For more information: www.arrs.org


 February 20, 2026
February 20, 2026