Latest additions to Somatom go. CT platform address advanced clinical fields and applications, including cardiology, CT-guided intervention and dual energy CT.
Recent studies show a rapid increase in patient radiation exposure mainly due to increased use of medical imaging, particularly computed tomography (CT). Several high-profile cases in mainstream media covering radiation poisoning and burns due to extremely high CT doses have made dose a major concern. Vendors have responded by introducing technologies to greatly reduce CT dose. “There is no other imaging technology that has put as much effort into making CT a safe technology for us today while maintaining image quality,” said CT imaging expert Leslee Shaw, Ph.D., FACC, FASNC, FAHA, co-director of the Emory Clinical Cardiovascular Research Institute.
Cardiac exams have historically had the highest dose of any CT exam performed, with average doses of 15 millisieverts (mSv) or higher. These scans can now be performed with doses of 1 mSv or less on the latest equipment in some patients. “I think it is important to understand the differences and to consider the newer technologies, particularly from a safety point-of-view to do very low-dose imaging,” Shaw continued. If a hospital tends to have a large obese patient population, dose-lowering technologies can help significantly reduce CT dose. “The exposures we are using today for CTs of obese patients are not where they could be with the newer technologies that are now available.”
New CT systems also should be a selling point to patients in the community to promote the hospital as being on the cutting-edge of imaging technology. “There is a lot of concern today about the overuse of CT and overexposure of patients to radiation,” she said. “So, having that as a marketing piece that you are very concerned about patient-centered imaging and safety, and that you are using new technology to decrease dose — that is something you can make a great business case for. Or, to tell people that you are updating your technology to look for precisely improved patient care.”
New CT Systems
In the past 12 months, several CT vendors have introduced new systems with the latest in dose reduction hardware and software.
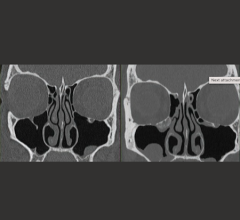
Canon Medical Systems. The Aquilion One/Genesis Edition computed tomography (CT) system from Canon Medical Systems (formerly Toshiba) gives clinicians the potential to diagnose and evaluate acute stroke quickly. The system is capable of imaging the entire brain with a single 640-slice rotation with ConeXact, covering 16 cm. It can also capture both anatomy and function, which provides physicians with additional tools to help diagnose stroke with a single CT scan, and may reduce the need for multimodality exams, which can take a significant amount of time.
The Aquilion One/Genesis Edition helps clinicians improve the diagnosis and evaluation of acute stroke, thanks to features that offer clinicians whole-brain stroke characterization in one examination. This includes Neuro One Protocol, which allows acquisition of multiple low-dose volume scans of the entire brain during contrast infusion to provide whole-brain perfusion and whole-brain dynamic vascular analysis in one exam; and forward projected FIRST model-based iterative reconstruction solution (MBIR) to improve high-contrast spatial resolution and low-contrast detectability in the brain, opening doors for the possibility of seeing early signs of stroke with CT. FIRST provides noise reduction and lowers radiation dose up to 82.4 percent as compared to filtered back projection (FBP), and removes workflow challenges of MBIR.
In April, Canon received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for the Aquilion Precision system, which it calls the world’s first ultra high-resolution computed tomography (UHR CT) system. The system can resolve anatomy as small as 150 microns and is designed to provide more than twice the resolution, typically seen only in cath labs. Containing an all-new detector as well as tube, gantry and reconstruction technologies, the system may make it possible to help expand visualization of disease thanks to new features that offer improved image detail.
The Aquilion Precision CT system emphasizes dose efficiency with detector channels that are only 0.25 mm thick. This, combined with substantial improvements in scintillator quantum efficiency and detector circuitry, results in a dose-efficient detector with ultra-high resolution capabilities. The system features low resolution not typically seen in CT imaging, according to Canon, with what it calls the industry’s smallest focal spot tube at 0.4 mm x 0.5 mm and the industry’s first routine 1,024 x 1,024 reconstruction matrix.
Siemens Healthineers. The FDA has cleared the Somatom go.All and Somatom go.Top CT systems from Siemens Healthineers. These additions to the company’s go. CT platform expand its concept of patient-centric mobile workflow, controlled via tablet and remote, into advanced clinical fields and applications such as cardiology, CT-guided intervention and dual-energy CT.
With a 0.33-second rotation time and a 75 kW generator, the 64-slice Somatom go.All does meet a wide range of clinical needs. The 128-slice Somatom go.Top leverages the same technologies as well as a large detector to deliver an acquisition speed of up to 175 mm in one second, making it ideal for trauma scanning. Interventional procedures benefit from Guide&Go, what Siemens calls the first tablet-based solution for CT-guided interventions, which enables the interventional radiologist to use traditional touch features rather than a joystick for more precise image manipulation.
Somatom go.Top offers TwinBeam Dual Energy imaging for simultaneous examination of the same region at two different energy levels. Each of the four scanners in the Somatom go. CT platform uses GO technologies such as Recon&GO to reduce the time a technologist spends on manual and repetitive reconstruction tasks. The platform enables zero-click reconstructions for even highly complex procedures such as coronary CT angiography and TwinBeam Dual Energy, helping the technologist remain close to — and focus on — patients.
In addition, the FDA has cleared the latest version of the Somatom Force, the flagship dual-source CT system from Siemens. The system now features the new FAST (Fully Assisting Scanner Technologies) Integrated Workflow, which helps ensure precise patient positioning. A key component of the FAST Integrated Workflow is the new FAST 3-D Camera. The camera fits above the patient table and uses artificial intelligence and deep learning to enable automatic, precise and consistent isocentric positioning of patients. Touch panels fitted on the gantry allow staff to leverage this automation at the push of a button while remaining close to the patient during scan preparation.
The updated Somatom Force also offers iterative metal artifact reduction (iMAR), enabling users to significantly reduce artifacts caused by metal implants, artificial joints or pacemakers. Additionally, the improved image reconstruction system (IRS) reconstructs up to 70 images per second with iterative reconstruction.
The new FAST Integrated Workflow with the FAST 3-D Camera also will be available with the Somatom Drive dual source CT system. It was already approved on the Somatom Edge Plus in early April 2018.
This article was originally published as an introduction to the CT Dose Management comparison chart. You can view the chart here.


 March 03, 2026
March 03, 2026