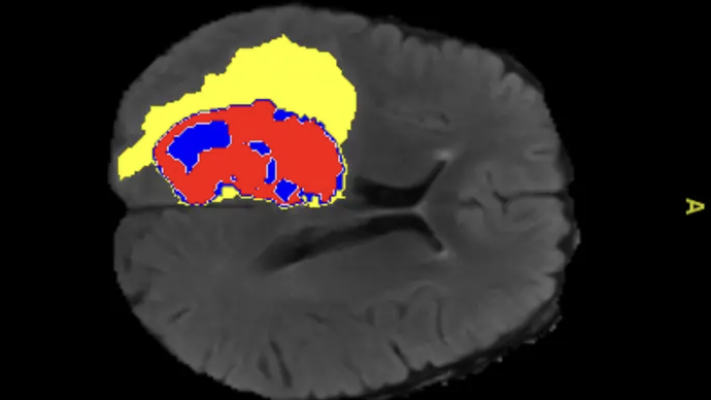
AI-annotated medical image showing enhanced tumor, tumor core and edema regions. Image courtesy of Monash University
July 26, 2023 — Researchers at Monash University have designed a new co-training AI algorithm for medical imaging that can effectively mimic the process of seeking a second opinion.
Published recently in Nature Machine Intelligence, the research addressed the limited availability of human annotated, or labelled, medical images by using an adversarial, or competitive, learning approach against unlabeled data.
This research, by Monash University faculties of Engineering and IT, will advance the field of medical image analysis for radiologists and other health experts.
PhD candidate Himashi Peiris of the Faculty of Engineering, said the research design had set out to create a competition between the two components of a "dual-view" AI system.
“One part of the AI system tries to mimic how radiologists read medical images by labelling them, while the other part of the system judges the quality of the AI-generated labelled scans by benchmarking them against the limited labelled scans provided by radiologists,” said Peiris.
“Traditionally radiologists and other medical experts annotate, or label, medical scans by hand highlighting specific areas of interest, such as tumors or other lesions. These labels provide guidance or supervision for training AI models.
“This method relies on the subjective interpretation of individuals, is time-consuming and prone to errors and extended waiting periods for patients seeking treatments.”
The availability of large-scale annotated medical image datasets is often limited, as it requires significant effort, time and expertise to annotate many images manually.
The algorithm developed by the Monash researchers allows multiple AI models to leverage the unique advantages of labelled and unlabeled data, and learn from each other's predictions to help improve overall accuracy.
“Across the three publicly accessible medical datasets, utilizing a 10 per cent labelled data setting, we achieved an average improvement of 3 per cent compared to the most recent state-of-the-art approach under identical conditions,” said Peiris.
“Our algorithm has produced groundbreaking results in semi-supervised learning, surpassing previous state-of-the-art methods. It demonstrates remarkable performance even with limited annotations, unlike algorithms that rely on large volumes of annotated data.
“This enables AI models to make more informed decisions, validate their initial assessments, and uncover more accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions.”
The next phase of the research will focus on expanding the application to work with different types of medical images and developing a dedicated end-to-end product that radiologists can use in their practices.
The study published in Nature Machine Intelligence was led by Associate Professor Mehrtash Harandi and conducted by principal researcher, Himashi Peiris, a Ph.D. candidate at Monash University’s Faculty of Engineering, together with Associate Professor Zhaolin Chen, Dr Munawar Hayat and Professor Gary Egan, from Monash Biomedical Imaging and the Faculty of Information Technology.
For more information: https://www.monash.edu/


 March 11, 2026
March 11, 2026 









