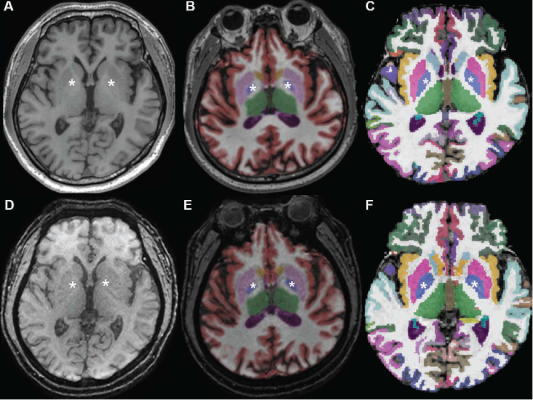
Conventional 3D T1W image (A) without segmentation, (B) with segmentation by Neuroquant, and (C) with segmentation by Freesurfer; ultrafast 3D-EPI T1W image (D) without segmentation, (E) with segmentation by Neuroquant, and (F) with segmentation by Freesurfer. Pallidum (asterisks) appears larger for Freesurfer (C, F) than for NeuroQuant (B, E), but appears similar in size between two sequences for each software package. For both software packages, bilateral frontal and occipital cortices (B, C) at bone-tissue interface appear more color-coded for conventional than for ultrafast sequence, contributing to larger cortical gray matter for conventional sequence
January 5, 2022 — According to an article in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), brain volume measurements in memory-impaired patients show significant differences and systematic biases between conventional and ultrafast 3D T1-weighted (T1W) MRI sequences.
“In patients for whom severe motion artifact precludes use of the conventional sequence, the ultrafast sequence may be useful to enable brain volumetry,” wrote corresponding author Hye Jin Baek of Gyeongsang National University and Changwon Hospital in Korea. “However, the current conventional 3D T1W sequence remains preferred in patients who can tolerate the standard examination.”
To compare automated brain volume measurements between conventional 3D T1W and ultrafast 3D echo-planar imaging (EPI) T1W sequences, Baek and colleagues retrospectively studied 36 patients (25 women, 11 men; mean age, 68 years) with memory impairment who underwent 3-T brain MRI. Examinations included both isotropic 3D T1W using inversion recovery gradient-recalled echo sequence (slice, 1.0 mm; acquisition, 3:04) and, in patients exhibiting motion, isotropic 3D EPI T1W sequence (slice, 1.2 mm; acquisition, 0:30). Using NeuroQuant (CorTechs Labs) and FreeSurfer (Harvard University) software to automate brain segmentation, measurements were compared between sequences for nine regions in each hemisphere.
For automated brain volumetry from ultrafast 3D EPI T1W imaging, compared with conventional 3D T1W imaging, most regions demonstrated at least substantial agreement between the two sequences—yet also significantly different mean values, moderate or large effect sizes, and consistent systematic biases with wide limits of agreement.
“The variation between the two sequences was observed in subset analyses of 16 patients with, and 20 patients without, Alzheimer disease,” the authors of this AJR article added.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









