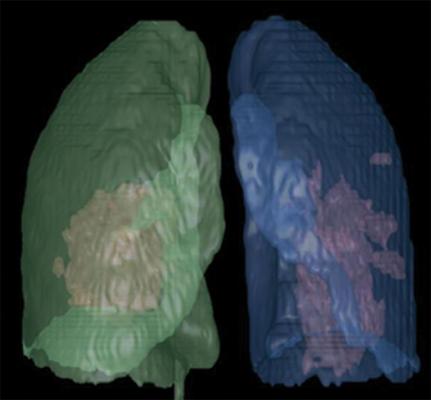
Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted software was used to identify inflammatory tissues in lung and automatically segment inflammatory lesions. Three-dimensional image shows regions of COVID-19 pneumonia in lung through AI postprocessing. Image courtesy of the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
July 10, 2020 — An open-access American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) article investigating the differences in computed tomography (CT) findings between coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia and influenza virus pneumonia found that most lesions from COVID-19 were located in the peripheral zone and close to the pleura, whereas influenza virus was more prone to show mucoid impaction and pleural effusion.
"However," lead author Liaoyi Lin of China's First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University cautioned, "differentiating between COVID-19 pneumonia and influenza virus pneumonia in clinical practice remains difficult."
A total of 97 patients (49 women, 48 men) were enrolled in this study. Of them, 52 patients (29 men, 23 women; age range, 21-73 years) had COVID-19 pneumonia; 45 patients (26 women, 19 men; age range, 15-76 years) had influenza virus pneumonia (28, influenza A; 17, influenza B). All patients had positive nucleic acid testing results for the respective viruses, as well as complete clinical data and CT images.
According to Lin and colleagues: "Between the group of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and the group of patients with influenza virus pneumonia, the largest lesion close to the pleura (i.e., no pulmonary parenchyma between the lesion and the pleura), mucoid impaction, presence of pleural effusion, and axial distribution showed statistical difference (p < 0.05)."
Meanwhile, Lin et al. noted that the properties of the largest lesion, presence of ground-glass opacities, consolidation, mosaic attenuation, bronchial wall thickening, centrilobular nodules, interlobular septal thickening, crazy paving pattern, air bronchogram, unilateral or bilateral distribution, and longitudinal distribution did not show significant differences (p > 0.05).
Additionally, the authors observed no significant difference (p > 0.05) in CT score, length of the largest lesion, mean density, volume, or mass of the lesions between the two groups.
Because the CT manifestations of COVID-19 and influenza virus so often overlap, "even with the characteristics evaluated using AI software," Lin et al. wrote, "no significant differences were detected."
Thus, the authors of this AJR article concluded that the more important role of CT during the present pandemic is in finding lesions and evaluating the effects of treatment.
For more information: www.

 March 09, 2026
March 09, 2026 









