
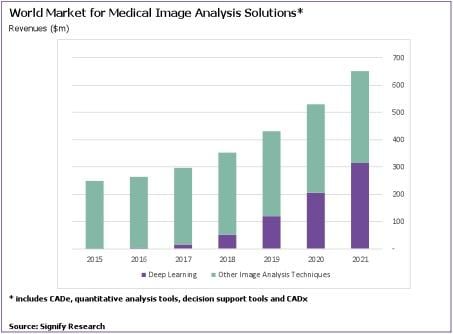
February 15, 2017 — Deep learning, also known as artificial intelligence, will increasingly be used in the interpretation of medical images to address many long-standing industry challenges. This will lead to a $300 million market by 2021, according to a new report by Signify Research, an independent supplier of market intelligence and consultancy to the global healthcare information technology industry.
In most countries, there are not enough radiologists to meet the ever-increasing demand for medical imaging. Consequently, many radiologists are working at full capacity. The situation will likely get worse, as imaging volumes are increasing at a faster rate than new radiologists entering the field. Even when radiology departments are well-resourced, radiologists are under increasing pressure due to declining reimbursement rates and the transition from volume-based to value-based care delivery. Moreover, the manual interpretation of medical images by radiologists is subjective, often based on a combination of experience and intuition, which can lead to clinical errors.
A new breed of image analysis software that uses advanced machine learning methods, e.g. deep learning, is tackling these problems by taking on many of the repetitive and time-consuming tasks performed by radiologists. There is a growing array of “intelligent” image analysis products that automate various stages of the imaging diagnosis workflow. In cancer screening, computer-aided detection can alert radiologists to suspicious lesions. In the follow-up diagnosis, quantitative imaging tools provide automated measurements of anatomical features. At the top-end of the scale of diagnostic support, computer-aided diagnosis provides probability-driven, differential diagnosis options for physicians to consider as they formulate their diagnostic and treatment decisions.
“Radiology is evolving from a largely descriptive field to a more quantitative discipline. Intelligent software tools that combine quantitative imaging and clinical workflow features will not only enhance radiologist productivity, but also improve diagnostic accuracy,” said Simon Harris, principal analyst at Signify Research and author of the report.
However, it is early days for deep learning in medical imaging. There are only a handful of commercial products and it is uncertain how well deep learning will cope with variations in patient demographics, imaging protocols, image artifacts, etc. Many radiologists were left underwhelmed by early-generation computer-aided detection, which used traditional machine learning and relied heavily on feature engineering. They remain skeptical of machine learning’s abilities, despite the leap in performance of today’s deep learning solutions, which automatically learn about image features from radiologist-annotated images and a "ground-truth”. Furthermore, the “black box” nature of deep learning and the lack of traceability as to how results are obtained could lead to legal implications. While none of these problems are insurmountable, healthcare providers are likely to take a ‘wait and see’ approach before investing in deep learning-based solutions.
“Deep learning is a truly transformative technology and the longer-term impact on the radiology market should not be underestimated. It’s more a question of when, not if, machine learning will be routinely used in imaging diagnosis”, Harris concluded.
“Machine Learning in Medical Imaging – 2017 Edition” provides a data-centric and global outlook on the current and projected uptake of machine learning in medical imaging. The report blends primary data collected from in-depth interviews with healthcare professionals and technology vendors, to provide a balanced and objective view of the market.
For more information: www.signifyresearch.net



 March 11, 2026
March 11, 2026 









