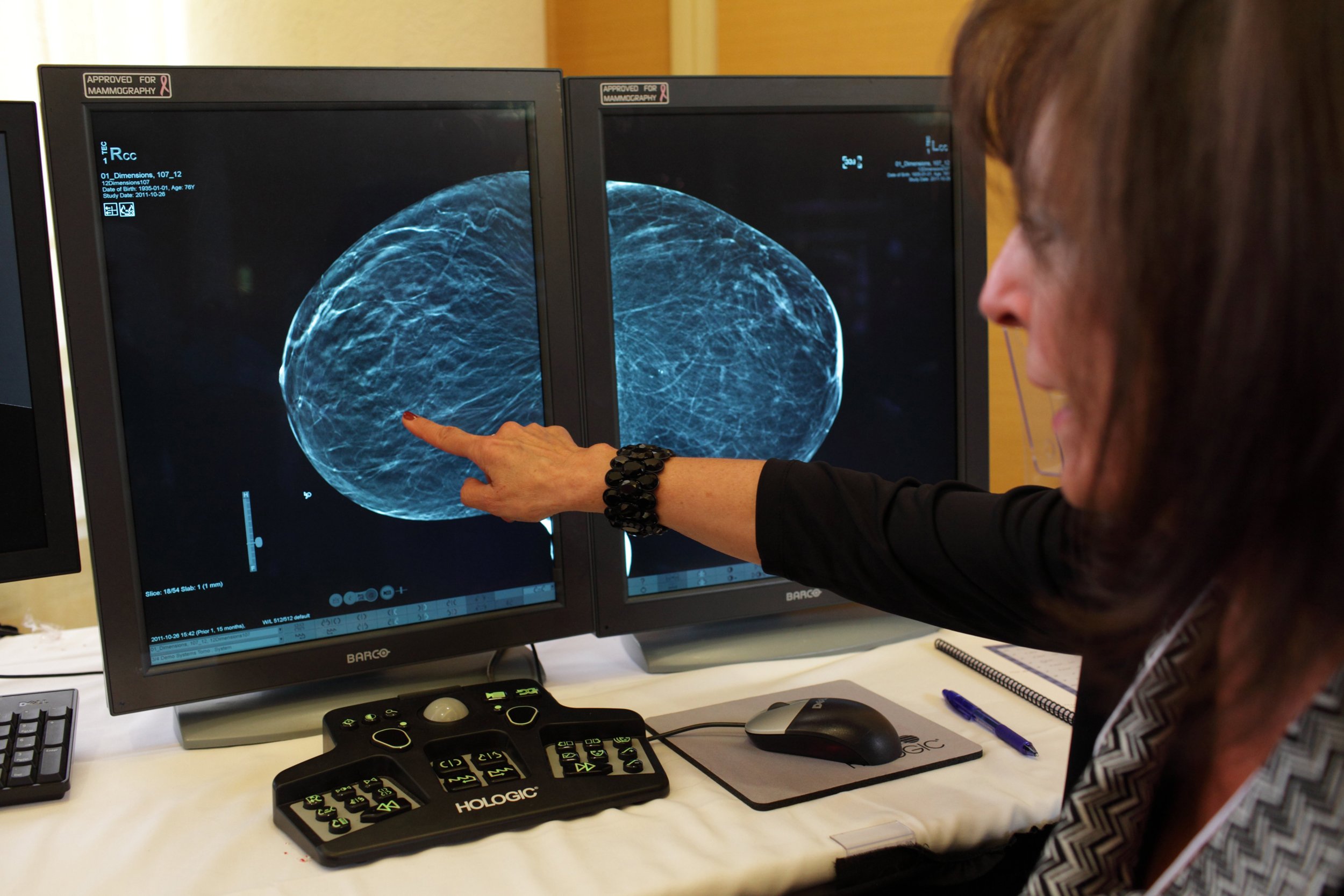
August 1, 2013 — Digital tomosynthesis is an effective tool for reducing the recall rate in breast cancer screening, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
Digital breast tomosynthesis has shown promise at reducing recall rates, particularly in younger women and in those with dense breast tissue. Tomosynthesis is similar to mammography in that it relies on ionizing radiation to generate images of the breast. However, unlike conventional mammography, tomosynthesis allows for three-dimensional (3-D) reconstruction of the breast tissue, which can then be viewed as sequential slices through the breast.
In the study, Brian M. Haas, M.D., worked with Liane E. Philpotts, M.D., both of Yale University School of Medicine, and other colleagues to compare screening recall rates and cancer detection rates in two groups of women: those who received conventional digital mammography alone and those who had tomosynthesis in addition to mammography.
Of the 13,158 patients who underwent screening mammography, 6,100 received tomosynthesis. The cancer detection rate was 5.7 per 1,000 in patients receiving tomosynthesis, compared with 5.2 per 1,000 in patients receiving mammography alone.
The addition of tomosynthesis resulted in a 30 percent reduction in the overall recall rate, from 12 percent for mammography alone to 8.4 percent in the tomosynthesis group.
Tomosynthesis has one significant drawback: a radiation dose approximately double that of digital mammography alone. However, Haas noted that new technology approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration could reduce the dose.
"The technology involves taking the tomosynthesis data and collapsing it into planar imaging that resembles 2-D mammography," he said. "It has the potential to eliminate the need for acquisition of the conventional 2-D images in addition to the tomosynthesis images."
The research group is currently in the process of comparing the cancers found on tomosynthesis with those found on mammography. They are also tracking the study group for interval cancers — those that develop in the interval between screenings — to make sure that the reduced recall rate associated with tomosynthesis is not resulting in missed cancers.
For more information: www.RadiologyInfo.org


 February 18, 2026
February 18, 2026