December 1, 2020 — The study "Will We Solve Crimes with Radiomics? Results of an Experimental Study on Charred Human Bone Samples," was presented at the Virtual Radiological Society of North America's 2020 conference (RSNA20). Radiomics, which extracts data from clinical images, can be reliably used to assess changes in the bone structure due to fire exposure. Specific features can be applied to determine the interval of combustion.
Combustion is often applied to conceal corpses after murders. Therefore, establishing the timing of the combustion can provide fundamental details in forensic investigations. This study assesses the role of radiomics in characterizing time-related changes occurring in human bone samples exposed to fire and proposes a method that can be applied to provide additional information useful in determining the time and cause of death.
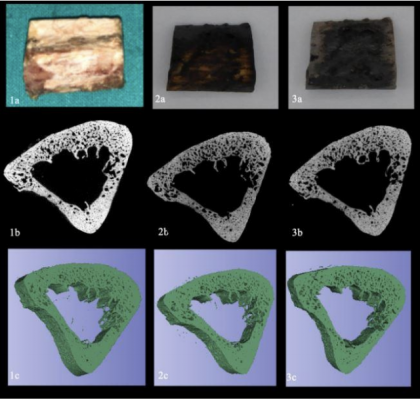
Fifteen samples of human fibulae were examined by a high-resolution micro-CT before and after direct exposure to fire for three combustion intervals. (Three samples were excluded after fragmentation during the second combustion.) From each sample, at each combustion interval, bone density and volume and 55 radiomic features were extracted. The results showed that radiomics was able to detect changes in the bone samples dependent on time of exposure to the fire.
The authors include Amalia Lupi, M.D., Presenter, Arianna Giorgetti, Guido Viel, M.D., Ph.D., Giovanni Cecchetto, M.D., Roberto Stramare, M.D., Chiara Giraudo, M.D., Ph.D.
For more information: www.rsna.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026