July 16, 2025 — Artificial intelligence can improve diagnostic consistency and reduce false-positives in prostate cancer detection, according to an accepted manuscript published in the American Roentgen Ray Society’s American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
Noting enhanced clinical utility for radiologists, “AI may enhance consistency and reduce false-positives in prostate biparametric MRI (bpMRI) interpretation,” clarified AJR corresponding author Baris Turkbey, MD, from the National Cancer Institute and National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, MD. “Further optimization is required to improve sensitivity without compromising specificity.”
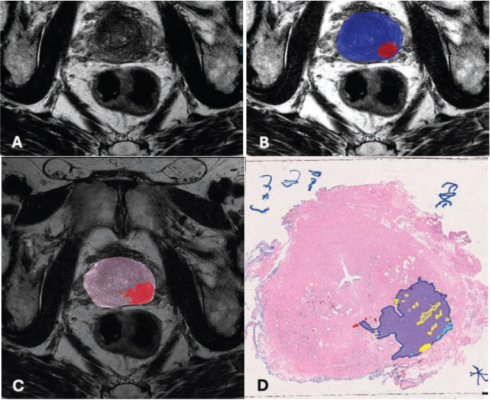
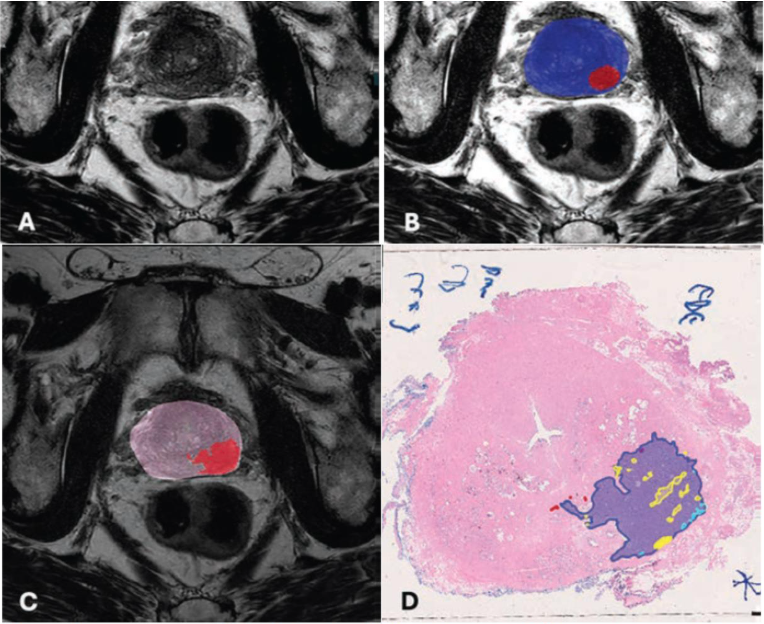
Turkbey et al.’s multireader, multicenter study used a balanced incomplete block design for MRI randomization. Six radiologists of varying experience interpreted bpMRI scans with and without AI assistance in alternating sessions. The reference standard for lesion-level detection for cases was whole-mount pathology after radical prostatectomy; for control patients, negative 12-core systematic biopsies. In all, 180 patients (120 case group, 60 control group) who underwent mpMRI and prostate biopsy or radical prostatectomy between January 2013 and December 2022 were included. The AJR authors then assessed lesion-level sensitivity, PPV, patient-level AUC for clinically significant prostate cancer and prostate cancer detection, and interreader agreement in lesion-level PI-RADS scores and size measurements.
Ultimately, AI-assisted bpMRI interpretation improved lesion-level PPV for prostate cancer (PI-RADS ≥ 3: 80.9% vs. 69.4%, p < .001) and significantly enhanced interreader agreement for PI-RADS scoring (κ = 0.748 vs. 0.336, p < .001) but slightly reduced sensitivity.
A supplement to this AJR manuscript is available online.


 March 09, 2026
March 09, 2026 









