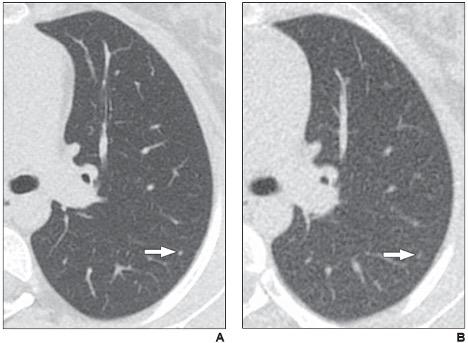
Axial reformatted clinical (1.083 mSv) and reduced dose (0.318 mSv) CT images from a 17-year-old girl with osteosarcoma. A 2 mm left lower lobe nodule is clearly visible in the left lower lobe on the clinical CT image (arrow in A). The same nodule is vaguely apparent on the reduced-dose CT image (arrow in B), classified as present but poorly visible.
July 9, 2021—According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), reduced-dose CT depicts greater than 90% of lung nodules in children and young adults with cancer, identifying the presence of nodules with moderate sensitivity and high specificity.
“CT performed at 0.3 mSv mean effective dose has acceptable diagnostic performance for lung nodule detection in children and young adults and has the potential to reduce patient dose or expand CT utilization (e.g., to replace radiography in screening or monitoring protocols),” wrote corresponding author Andrew T. Trout of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center in Ohio.
Trout and colleagues’ prospective study enrolled patients 4–21 years old with known or suspected malignancy who were undergoing clinically indicated chest CT. Study participants underwent an additional investigational reduced-dose chest CT in the same imaging encounter. Three independent radiologists blind-reviewed the separated and deidentified CT examinations, with one radiologist performing a subsequent review to match nodules between the standard- and reduced-dose examinations.
Among the 78 patients (44 male, 34 female; mean age, 15.2 years) with cancer who underwent standard-dose chest CT and reduced-dose chest CT (mean effective dose 0.3 ± 0.1 mSv, representing 83% dose reduction) in the same imaging encounter, the reduced-dose protocol detected greater than 90% of lung nodules identified on the standard-dose examination.
Noting that no prior study has directly compared clinical to reduced-dose CT for detection of lung nodules in children, “reduced-dose CT may be a feasible option for detection of pulmonary metastatic disease in situations in which radiation dose is a primary consideration or as an option to reduce dose in patients undergoing serial chest CT to monitor known disease,” the authors of this AJR article concluded.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026