January 29, 2020 – The presence of a blood clot on the wall of the aorta in people with abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) is associated with more rapid, potentially dangerous growth in the aneurysm, according to a major study published Jan. 28 in the journal Radiology.[1] Researchers said the findings could help identify which patients need more aggressive treatment and more frequent follow-up imaging after their initial diagnosis.
The aorta is the major artery that carries oxygenated blood from the heart. Abdominal aneurysms occur when a bulge forms in the portion of the artery that runs through the abdomen. About 200,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with the condition every year. Over time, the wall can weaken and rupture. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm is the 10th leading cause of death for men over age 55.
Decisions to surgically repair the aneurysm are based on its diameter. Patients with aneurysms larger than 5.5 cm are normally referred for repair, while those smaller than 5.5 cm are most commonly monitored with imaging at regular intervals. Ultrasound and cross-sectional imaging with CT or MRI are commonly used.
However, this diameter-based management strategy has limitations, as a considerable number of small aneurysms rupture, according to the study’s first author, Chengcheng Zhu, Ph.D., assistant researcher from the Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging at the University of California in San Francisco.
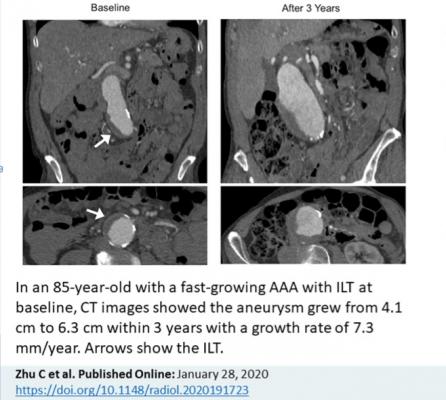
Zhu and colleagues focused their study on the intraluminal thrombus, a blood clot on the wall of the aorta at the location of the aneurysm. Intraluminal thrombi are present in the majority of aneurysms close to the repair threshold of 5.5 cm, and in a considerable number of smaller aneurysms. Despite their prevalence, the influence of these clots on abdominal aortic aneurysm growth and rupture risk is still not fully understood.
“Intraluminal thrombus could be a new marker for aneurysm growth,” Zhu said.
The researchers used high resolution cross-sectional imaging with CT or MRI to assess 225 men with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Follow-up lasted, on average, more than three years.
Slightly more than half of patients had an intraluminal thrombus. The aneurysms of those with intraluminal thrombus were larger at baseline and grew by a rate of 2 mm per year, twice as fast as the 1 mm per year growth rate in people without intraluminal thrombus.
“An aneurysm with thrombus grows much faster than one without a thrombus,” Zhu said. “Our study looked at a large number of patients with a relatively long follow-up to confirm that thrombus is a new risk factor that may be potentially reported by radiologists.”
While the study did not examine the reasons why the presence of a thrombus had such a dramatic impact on aneurysms, Zhu noted that it likely has harmful biochemical effects on the vessel wall.
“When the vessel wall is covered with thrombus, the lack of oxygen weakens the wall of the vessel, making the aneurysm likely to grow faster and rupture,” he explained.
The findings suggest that imaging follow-up schedules may need to be adjusted for patients whose aneurysm has a thrombus. Current protocols for follow-up imaging are based on aneurysm size and do not account for the absence or presence of a thrombus.
“A patient at high risk may need closer monitoring,” Zhu said. “If in patients with a thrombus the aneurysm grows twice as fast, then shortening the surveillance interval could be considered.”
Zhu said more research is needed before thrombus detection is integrated into clinical protocols. For now, he said the findings provide another piece of information to use in determining the prognosis of patients with this potentially dangerous condition.
Reference:


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026