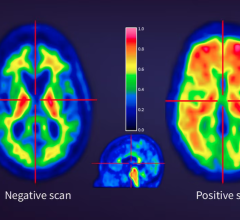
A study which found personalized dosing of prostate cancer resulting in improved patient outcomes was presented during the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2023 Annual Meeting, SNMMI 2023, held June 24-27 in Chicago, IL. This figure represents outcomes from response groups based on PSA and Lu SPECT at six weeks.
June 29, 2023 — A study presented this week during the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Annual Meeting, SNMMI 2023, found that personalized dosing of men with prostate cancer resulted in improved patient outcomes. Authors of the study reported that by monitoring early-response biomarkers in men undergoing 177Lu-PSMA prostate cancer treatment, physicians can personalize dosing intervals, significantly improving patient outcomes. In the study, early stratification with 177Lu-SPECT/CT allowed men responding to treatment to take a “treatment holiday” and allowed those not responding the option to switch to another treatment.
The research paper, “Patient outcomes following a response biomarker guided approach to treatment using 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in men with metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer (Re-SPECT)” was presented on June 27 during the meeting of the international scientific and medical organization representing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging.
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2022, 177Lu-PSMA is an effective treatment for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. However, not all men respond equally to treatment, with some responding very well and others progressing early.
“Currently, a standardized dosing interval is used for 177Lu-PSMA treatment,” said Andrew Nguyen, MBBS, FRACP, AANMS, senior staff specialist in the Department of Theranostics and Nuclear Medicine at St. Vincent's Hospital in Sydney, Australia. “However, monitoring early-response biomarkers to adjust treatment intervals may improve patient outcomes.”
In the study, researchers sought to evaluate progression-free survival and overall survival of different dosing intervals. Study participants included 125 men who were treated in a clinical program with six weekly doses of 177Lu-PSMA. The men were imaged with 177Lu-SPECT/CT after each dose. After the second dose, researchers analyzed the men’s prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels and the 177Lu-SPECT response to determine ongoing management.
Patients were grouped by level of response. Those in Response Group 1 (35 percent of participants) had a marked reduction in PSA level and partial response on 177Lu-SPECT and were advised to cease treatment until PSA levels rose. Response Group 2 (34 percent) saw stable or reduced PSA and stable disease on SPECT imaging; these men continued on their six-week treatment plan until no longer clinically beneficial. In Response Group 3 (31 percent), men saw a rise in PSA levels and had progressive disease on SPECT imaging. These patients were offered the opportunity to try a different treatment.
PSA levels decreased by more than 50 percent in 60 percent of patients. Overall study participants had a median PSA progression-free survival of 6.1 months and a median overall survival of 16.8 months. Median PSA progression-free survival was 12.1 months, 6.1 months, and 2.6 months, for Response Groups 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The overall survival was 19.2 months for Response Group 1, 13.2 months for Response Group 2, and 11. 2 months for Response Group 3. Additionally, for those in Response Group 1 who had a “treatment holiday,” the median treatment-free time was 6.1 months.
“Personalized dosing allowed one-third of the men in this study to have treatment breaks while still achieving the same progression-free and overall survival outcomes they would have if they received continuous treatment,” noted Nguyen. “It also allowed another one-third of men who had early biomarkers of disease progression the opportunity to try a more effective potential therapy if one was available.”
Patients at St. Vincent's Hospital will continue to be stratified by these early response biomarkers. Once validated in a prospective clinical trial, Nguyen hopes that this stratification strategy will become more widely available for patients.
Authors of the study were: Louise Emmett, Sarennya Pathmanandavel, Maria Ayers, and Andrew Nguyen, Department of Theranostics and Nuclear Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia; Nikeith John, William Counter, Aron Poole, Shikha Agrawal, and Lyn Chan, St. Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia; Peter Eu, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre. Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; Megan Crumbaker, The Kinghorn Cancer Centre, St. Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia.
More information: www.snmmi.org
Keep up with coverage of SNMMI 2023 news here.


 February 12, 2026
February 12, 2026