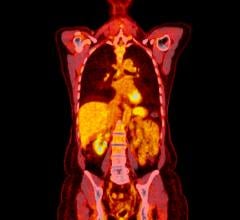
August 6, 2009 - Positron emission tomography (PET) is an important tool for depicting the extent of neuroblastoma in some patients, particularly for those in the early stages of the disease, reported a new study published in the August issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Neuroblastoma accounts for six to ten percent of all childhood cancers in the United States and 15 percent of cancer deaths in children. Accurately identifying where in the body the disease is located and whether it is spreading is critical for choosing appropriate types of treatment, which can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation and-in the most advanced cases-a combination of all of these treatments along with bone marrow transplant or investigational therapies.
In recent years, 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) has been the main functional imaging agent used to assess the disease. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET imaging of neuroblastoma is increasing, but questions remain regarding when and in which patients FDG PET imaging is most useful.
"Functional imaging plays an important role in assessing neuroblastoma, from initially diagnosing and staging the disease to determining whether patients are responding to treatment or whether the disease has recurred," said Susan E. Sharp, M.D., assistant professor of clinical radiology at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and lead author of the study. "Our study found that while MIBG remains the front-line imaging tool for neuroblastoma, FDG-PET imaging can benefit some patients, especially those with early-stage disease."
The study also found that FDG PET may also be useful in imaging neuroblastoma tumors that do not readily absorb MIBG. In these cases, imaging with MIBG alone may not reveal some malignant lesions in the body.
Neuroblastoma--a form of cancer that starts in certain types of very primitive developing nerve cells found in an embryo or fetus--occurs most frequently in infants and young children. There are about 650 new cases of the cancer reported in the U.S. each year, according to the National Cancer Institute. The cancer most often originates on the adrenal glands--the triangular-shaped glands above the kidneys. Neuroblastoma often spreads to other parts of the body before any symptoms are apparent.
Patients with the disease are classified as low-, medium- or high-risk based on a combination of clinical staging of the disease and certain biologic and genetic characteristics, such as the age of the patient, extent of disease spread, microscopic appearance and genetic factors.
Treatment for each of the risk categories is very different. If the cancer is limited to one part of the body, it is often curable with surgery, sometimes with the addition of chemotherapy. However, long-term survival for children older than 18 months of age with advanced disease is poor despite aggressive treatments that include a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, bone marrow transplant and investigational therapies.
In the study, a total of 113 paired MIBG scans and FDG PET scans in 60 patients with neuroblastoma at two major pediatric cancer institutions were reviewed. PET was used in conjunction with localization computerized tomography (CT) scans, and MIBG planar and SPECT imaging were combined. The study shows that for stage 1 and stage 2 neuroblastoma patients, FDG-PET depicted more primary or residual neuroblastoma, although MIBG imaging may be needed to exclude higher-stage disease that has spread to the bone or bone marrow. MIBG is superior in evaluating stage 4 neuroblastoma, primarily because it can detect and follow the response to treatment of tumor in the bone or bone marrow more accurately.
Citation: S. Sharp, B. Shulkin, M. Gelfand, S. Salisbury, W. Furman, Departments of Radiology and Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati; and Departments of Radiological Sciences and Oncology, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis "123 I-MIBG Scintigraphy and 18F-FDG PET in Neuroblastoma," The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, August 2009.
For More Information: www.snm.org


 February 27, 2026
February 27, 2026