
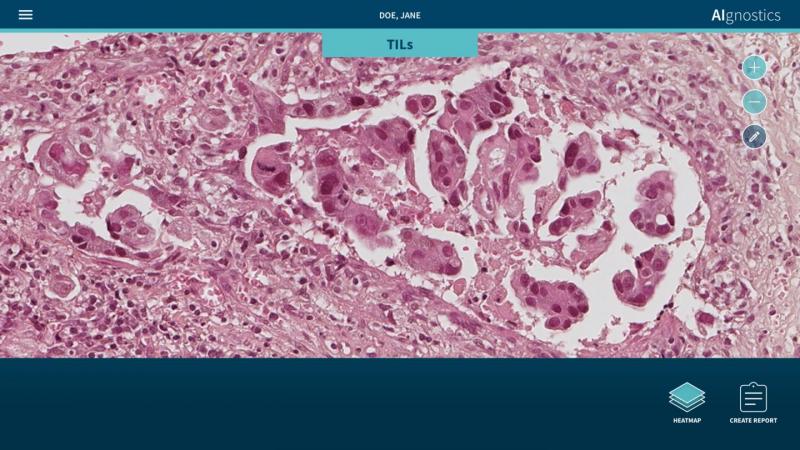
Detection of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) using explainable AI. The AI-technique is used to generate a heatmap showing TILs (red) and other tissues and cells (blue and green). Image courtesy of Klauschen/Charité
March 22, 2021 — Researchers at Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and TU Berlin as well as the University of Oslo have developed a new tissue-section analysis system for diagnosing breast cancer based on artificial intelligence (AI). Two further developments make this system unique: For the first time, morphological, molecular and histological data are integrated in a single analysis. Secondly, the system provides a clarification of the AI decision process in the form of heatmaps. Pixel by pixel, these heatmaps show which visual information influenced the AI decision process and to what extent, thus enabling doctors to understand and assess the plausibility of the results of the AI analysis. This represents a decisive and essential step forward for the future regular use of AI systems in hospitals. The results of this research have now been published in Nature Machine Intelligence.
Cancer treatment is increasingly concerned with the molecular characterization of tumor tissue samples. Studies are conducted to determine whether and/or how the DNA has changed in the tumor tissue as well as the gene and protein expression in the tissue sample. At the same time, researchers are becoming increasingly aware that cancer progression is closely related to intercellular cross-talk and the interaction of neoplastic cells with the surrounding tissue - including the immune system.
Although microscopic techniques enable biological processes to be studied with high spatial detail, they only permit a limited measurement of molecular markers. These are rather determined using proteins or DNA taken from tissue. As a result, spatial detail is not possible and the relationship between these markers and the microscopic structures is typically unclear. "We know that in the case of breast cancer, the number of immigrated immune cells, known as lymphocytes, in tumor tissue has an influence on the patient's prognosis. There are also discussions as to whether this number has a predictive value - in other words if it enables us to say how effective a particular therapy is," said Prof. Frederick Klauschen, M.D., of Charité's Institute of Pathology.
"The problem we have is the following: We have good and reliable molecular data and we have good histological data with high spatial detail. What we don't have as yet is the decisive link between imaging data and high-dimensional molecular data," added Prof. Klaus-Robert Müller, M.D., professor of machine learning at TU Berlin. Both researchers have been working together for a number of years now at the national AI center of excellence the Berlin Institute for the Foundations of Learning and Data (BIFOLD) located at TU Berlin.
It is precisely this symbiosis which the newly published approach makes possible. "Our system facilitates the detection of pathological alterations in microscopic images. Parallel to this, we are able to provide precise heatmap visualizations showing which pixel in the microscopic image contributed to the diagnostic algorithm and to what extent," explained Müller. The research team has also succeeded in significantly further developing this process: "Our analysis system has been trained using machine learning processes so that it can also predict various molecular characteristics, including the condition of the DNA, the gene expression as well as the protein expression in specific areas of the tissue, on the basis of the histological images.
Next on the agenda are certification and further clinical validations - including tests in tumor routine diagnostics. However, Klauschen is already convinced of the value of the research: "The methods we have developed will make it possible in the future to make histopathological tumor diagnostics more precise, more standardized and qualitatively better."
For more information: www.
Related Breast Cancer/AI Workflow Content:
VIDEO: Integrating Artificial Intelligence Into Radiologists Workflow


 March 11, 2026
March 11, 2026 









