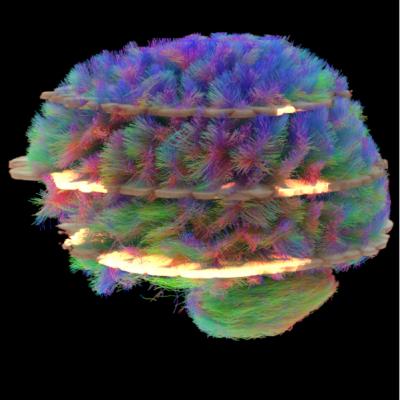
April 21, 2016 — Using a sophisticated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique, researchers have found abnormalities in the brain’s white matter tracts in patients with insomnia. Results of the study were published online in the journal Radiology.
Primary insomnia, in which individuals have difficulty falling or staying asleep for a month or longer, is associated with daytime fatigue, mood disruption and cognitive impairment. Insomnia can also lead to depression and anxiety disorders.
“Insomnia is a remarkably prevalent disorder,” said researcher Shumei Li, M.S., from the Department of Medical Imaging, Guangdong No. 2 Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, China. “However, its causes and consequences remain elusive.”
For the study, Li, along with colleagues lead by investigator Guihua Jiang, M.D., set out to analyze the white matter tracts in insomnia patients and the relationship between abnormal white matter integrity and the duration and features of insomnia.
“White matter tracts are bundles of axons — or long fibers of nerve cells — that connect one part of the brain to another,” Li said. “If white matter tracts are impaired, communication between brain regions is disrupted.”
The study included 23 patients with primary insomnia and 30 healthy control volunteers. To evaluate mental status and sleep patterns, all participants completed questionnaires including the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, the Insomnia Severity Index, the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale and the Self-Rating Depression Scale.
Each participant also underwent brain MRI with a specialized technique called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). DTI allows researchers to analyze the pattern of water movement along white matter tracts to identify a loss of tract integrity.
“We used a new method called Tract-Based Spatial Statistics that is highly sensitive to the microstructure of the white matter tract and provides multiple diffusion measures,” Li said.
Results of the analysis showed that compared to the healthy controls, the insomnia patients had significantly reduced white matter integrity in several right-brain regions and the thalamus, which regulates consciousness, sleep and alertness.
“These impaired white matter tracts are mainly involved in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness, cognitive function and sensorimotor function,” Li said.
In addition, abnormalities in the thalamus and body corpus callosum — the largest white matter structure in the brain — were associated with the duration of patients’ insomnia and score on self-rating depression scale.
“The involvement of the thalamus in the pathology of insomnia is particularly critical, since the thalamus houses important constituents of the body’s biological clock,” she added.
The study also found that underlying cause of white matter integrity abnormalities in insomnia patients may be loss of myelin, the protective coating around nerve fibers.
The researchers caution that further study needs to be done on a larger sample to clarify the relationship between altered white matter integrity and insomnia.
For more information: www.pubs.rsna.org/journa/radiology


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026