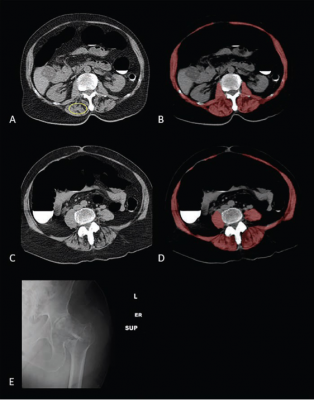
Sarcopenia (Myosteatosis) at Screening CT Colonoscopy in 79-Year-Old Woman With Subsequent Hip Fracture: A & B. Image at L1 vertebral level without (A) and with (B) overlay of automated skeletal muscle segmentation (B, red). Intramuscular fat is present within paraspinal muscles (A, yellow circle). Mean muscle attenuation is similar for manually placed ROI (1.8 HU) and automated tool (3.9 HU), being markedly decreased for both approaches. Muscle cross-sectional area is relatively preserved when intramuscular fat is included.
C & D. CT images at L3 level without (C) and with (D) muscle segmentation demonstrate similar findings.
E. Hip radiograph demonstrates left intertrochanteric femoral fracture that occurred when patient fell 2 years later. Patient died 4 years after falling.
August 19, 2021 — According to ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), use of the L1 vertebral level — typically included on both chest and abdominal computed tomography (CT) examinations—rather than the L3 level expands the reach of opportunistic CT screening for sarcopenia.
“Automated CT-based measurements of muscle attenuation for myosteatosis at the L1 level compare favorably with previously-established L3 level measurements and clinical risk scores for predicting hip fractures and death,” wrote lead investigator Perry J. Pickhardt from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health in Madison. “Assessment for myopenia was less predictive of outcomes at both levels.”
Pickhardt and colleagues’ retrospective study included 9,223 patients (4,071 men, 5,152 women; mean age, 57 years) who underwent unenhanced low-dose abdominal CT. Muscle assessment for myosteatosis (mean attenuation) and myopenia (cross-sectional area) at the L1 and L3 levels was done via a previously validated fully-automated deep learning tool. Performance for predicting hip fractures and death was compared between L1 and L3 measures, then evaluated using FRAX score and Framingham risk score, respectively.
Among the 9,223 asymptomatic adults who underwent abdominal CT, muscle attenuation measurements at the L1 and L3 levels showed similar utility in predicting subsequent hip fracture and death. Meanwhile, muscle attenuation measurements at both levels showed comparable performance as established clinical risk scores.
The assessment of muscle attenuation (myosteatosis) performed better than the assessment of muscle area (myopenia) “likely due in part to the automated tool’s inclusion of intramuscular fat within the segmented areas,” the authors of this AJR article added.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 February 16, 2026
February 16, 2026